Killian's dehiscence
Killian's dehiscence (also known as Killian's triangle) is a triangular area in the wall of the pharynx between the cricopharyngeus and thyropharyngeus which are the two parts of the inferior constrictors(also see Pharyngeal pouch). It can be seen as a locus minoris resistentiae. Similar triangular area between circular fibres of cricopharyngeus and longitudinal fibres of esophagus is Lamier's triangle or Lamier-hackermann's area.
| Killian's dehiscence | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of the pharynx and cheek. (Constrictor pharyngis inferior visible at bottom left.) | |
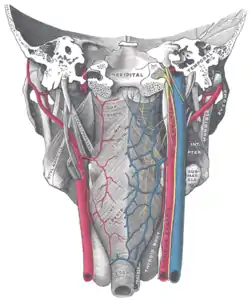 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves. (Inf. const. labeled at bottom center.) | |
| Anatomical terminology |
Clinical significance
It represents a potentially weak spot where a pharyngoesophageal diverticulum (Zenker's diverticulum) is more likely to occur.[1]
Eponym
It is named after the German ENT surgeon Gustav Killian.[2]
References
- Chaplin JM, Stewart IA (July 1994). "Use of surgical stapling device in excision of pharyngeal diverticulum". Aust N Z J Surg. 64 (7): 501–2. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1994.tb02266.x. PMID 8010924.
- synd/3707 at Who Named It?
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.