Jōtarō Watanabe
Jōtarō Watanabe (渡辺 錠太郎, Watanabe Jōtarō, April 16, 1874 – February 26, 1936) was a general in the early Shōwa period Imperial Japanese Army, noted as one of the victims of the February 26 Incident.
Jōtarō Watanabe | |
|---|---|
 General Watanabe Jōtarō | |
| Native name | 渡辺 錠太郎 |
| Born | April 16, 1874 Komaki, Aichi, Japan |
| Died | February 26, 1936 (aged 61) Tokyo, Japan |
| Allegiance | |
| Service/ | |
| Years of service | 1895–1936 |
| Rank | |
| Commands held | 7th Division Taiwan Army Inspector General of Military Training |
| Battles/wars | Russo-Japanese War |
Biography
Early career
Watanabe was a native of Komaki, Aichi, as the eldest of a tobacco merchant, Wada Takeemon. His father went bankrupt, and Watanabe was forced to quit middle school and was adopted by a farmer named Watanabe Shobei, taking his surname at the age of 19. At the age of 20 he was accepted as an officer cadet and graduated from the 8th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in June 1897.
On graduation, he was assigned to the IJA 19th Infantry Regiment and was promoted to lieutenant in November 1899. He entered the 17th class of the Army Staff College in December 1900. On graduation at the head of his class in December 1903, he was promoted to captain, and made a squad leader in the IJA 36th Infantry Regiment, which he accompanied to Manchuria during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905.
At the end of the war, he was reassigned to the Imperial General Headquarters and the following year was appointed as an aide to General Yamagata Aritomo. He was sent as a military attaché to China in 1906 and Germany in 1907, and was promoted to major in December 1908. Watanabe returned to Germany as a military attaché attached to the Japanese embassy in Berlin from May 1909 to June 1910, and on his return to Tokyo was assigned to the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff. In November 1910, Field Marshal Yamagata again requested that Watanabe be appointed as his aide, and Watanabe served Yamagata again until February 1915. In the interim, he was promoted to lieutenant colonel in June 1913.
In February 1915, after the start of World War I, Watanabe was assigned to the IJA 3rd Infantry Regiment. He transferred back to the General Staff in May 1916, and was promoted to colonel in July of the same year. In October 1917, he was sent as a military attaché to the Japanese embassy at Brussels, Belgium, where he was able to study first-hand on the effects of mechanized warfare.
As general
In August 1920, Watanabe was promoted to major general, and assumed command of the IJA 29th Infantry Brigade. He returned to the General Staff as Head of the 4th Bureau in September 1922. In May 1925, Watanabe was promoted to lieutenant general, and became commandant of the Army Staff College. In May 1926, he was commander of the IJA 7th Division. From March 1929, he commanded the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force, and from June 1930 was the commander of the Taiwan Army.
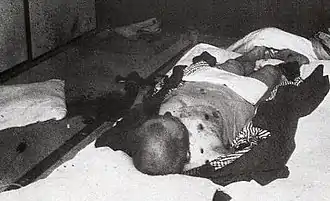
In August 1931, Watanabe was recalled to Tokyo and promoted to full general and military councilor with oversight over Army aviation. In July 1935, he was promoted to one of the most prestigious posts within the Imperial Japanese Army, that of Inspector General of Military Training, replacing Jinzaburō Masaki. Masaki was a close associate of General Sadao Araki and his Imperial Way Faction, promoting totalitarian, militarist, and expansionist ideals, whereas Watanabe had a reputation as a moderate. Many of the rebel officers of the February 26 Incident respected Masaki and blamed Watanabe for the personnel change. On his appointment, he gave a press conference in which he stated his belief that the Army should be under the control of the Ministry of the Army, thus implying his support for civilian control over the military, greatly incensing the Imperial Way Faction supporters.[1] Watanabe was the only active-duty military person on the rebel target list. Rebel soldiers surprised Watanabe at home in Ogikubo during the February 26 Incident, machine-gunning him to death in front of his wife and daughter. His grave is at Tama Cemetery in Tokyo. His daughter, Kazuko, was a classmate of future Empress Michiko, and later became a Catholic nun.
Watanabe was posthumously awarded the Order of the Rising Sun with Paulownia Flowers and given the honorific title of Junior Second Court Rank.[2]
Decorations
- 1934 –
 Order of the Golden Kite, 5th class [3]
Order of the Golden Kite, 5th class [3] - 1934 –
 Grand Cordon of the Order of the Rising Sun[4]
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Rising Sun[4] - 1936 –
 Order of the Rising Sun with Paulownia Flowers[5]
Order of the Rising Sun with Paulownia Flowers[5]
References
- Bix, Herbert P. (2001). Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan. Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-06-093130-2.
- Sims, Richard (2001). Japanese Political History Since the Meiji Renovation 1868-2000. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0-312-23915-7.
- Shillony, Ben-Ami. Revolt in Japan the young officers and the February 26, 1936 incident. Princeton, N.J: Princeton UP, 1973. Print. ISBN 0-691-07548-4
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jotaro Watanabe. |
- Ammenthorp, Steen. "Watanabe, Jotaro". The Generals of World War II.
Footnotes
- Byas, Hugh. Government by Assassination. Eschenburg Press. AISN B07BDNTDM4
- 『官報』第2747号「叙任及辞令」March 2, 1934
- 『官報』第2129号「叙任及辞令」February 8, 1934
- 『官報』第2129号「叙任及辞令」February 8, 1934
- 『官報』第2747号「叙任及辞令」March 2, 1936