Italian colonial railways
The Italian colonial railways started with the opening in 1888 of a short section of line in Italian Eritrea, and ended in 1943 with the loss of Italian Libya after the Allied offensive in North Africa and the destruction of the railways around Italian Tripoli. The colonial railways of the Kingdom of Italy reached 1,561 kilometres (970 mi) before WWII.
History
The construction of railways in the African Italian colonies (Eritrea, Libya and Somalia) did not have, for various reasons, a great development compared to that promoted by other European countries on the same continent.[1]
The first rail lines were built mainly for war needs in the absence of efficient means of communication in the occupied territories, after the conquests of Eritrea and Libya. However, were quite limited in the first decades of occupation. In 1940 the amount of railways in operation, between Italian East Africa and Libya, amounted to 1,556 km of which, however, the 693 km of the Italian section of the Railway Djibouti-Addis Ababa were pre-existing and built by the French Empire for Ethiopia.
The railways were built by Italy from the outset with little potential, because built with narrow gauge rails and with light metal type, and were never of great economic importance because isolated from the lines of neighboring states. Indeed, the choice of a gauge 950 mm (3 ft 1 3⁄8 in), different from the meter gauge usually used in Africa, contributed to this effect. Today most of these Italian colonial railways have disappeared: those of Somalia after the British occupation in 1941–1945. The Libyan ones were suppressed in the 1960s, but in the same decade the Eritrean railway between Italian Asmara and Massawa was reactivated after long neglect of trafficking.
Projects
In 1940 there were some projects of new colonial railways in the Italian Empire:
- Tripoli-Benghazi in Libya (1,000 km in construction since summer 1941)[2]
- Tripoli-border Tunisia (in construction since June 1941)
- Assab-Dire Dawa in Ethiopia & Eritrea
- Kassala-Agordat in Eritrea & Sudan[3]
Two international projects were studied for decades, but never done because of excessive financial difficulties:
- Italian "Transaharan railway" (Tripoli-Tchad/Camerun) between Libia and the Gulf of Guinea[4]
- Asmara-Addis Abeba-Mogadiscio (since the 1890s projected and allowed by international Treaties)[5]
All these projects were stopped by the WW2 defeat of Italy.
Italian colonial railways resumen
In 1940 the Italian colonial railways had 1,561 km and were the following:

| Railway name | Km | Years when built | Colony |
|---|---|---|---|
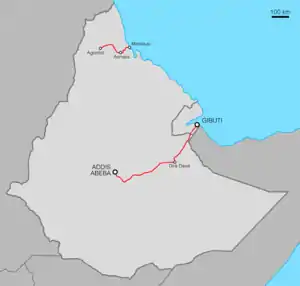
| Addis Abeba–Gibuti | 684 kmOnly Ethiopia section | 1902-1917 | |
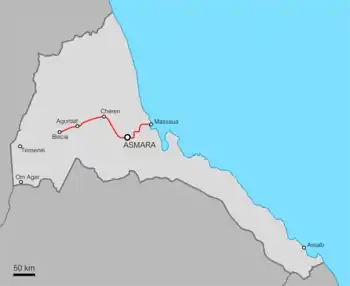
| Asmara–Biscia | 227 km | 1914–1932 | |
| Bengasi–Soluch | 56 km | 1926 | |
| Bengasi–Barce | 108 km | 1914–1927 | |
| Massaua–Asmara | 118 km | 1901–1911 | |
| Massaua–Saati | 26 km | 1886–1887 | |
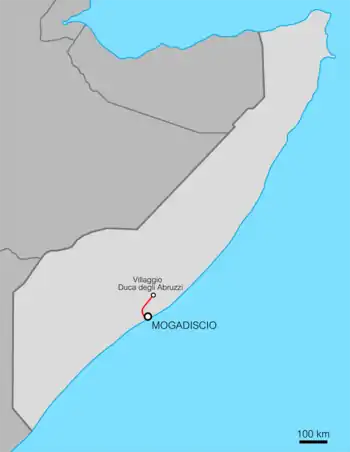
| Mogadiscio–Villaggio Duca degli Abruzzi | 113 km | 1924–1927 | |
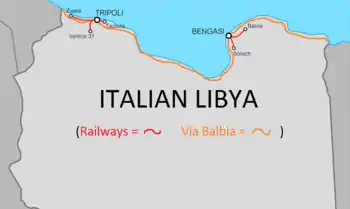
| Tripoli–Tagiura | 21 km | 1912 | |
| Tripoli–Vertice 31 | 90 km | 1912–1915 | |
| Tripoli–Zuara | 118 km | 1912–1919 | |
| Ferrovie coloniali italiane (Italian colonial railways) | 1,561 km |
With the above railways there were some decauville railways, like:
- Mersa Matuma–Kululi (Italian Eritrea): Nearly 90 km south of Massaua was built the so-called "Potash Transport Railway". It was a 42 kilometres (26 mi) long 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge potash transport railway built to serve the locations Adaito and Badda, located between Massawa and Assab. A Decauville gauge line was built in 1905 by the Italians inside the port of Mersa Fatuma and from it into the hinterland until Kululi (called "Colulli" in Italian) near the Ethiopian border.
- Villabruzzi–Ferfer (Italian Somalia). A small 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge railway of 250 km was constructed between Villabruzzi and the Somalia-Ethiopia border in order to solve the logistical problems related to the occupation of Ethiopia. In 1928–1936, the track was initially built in sections until Buloburde. The first railway section was 130 km long. It started in Bivio Adalei of the Mogadishu-Villaggio Duca degli Abruzzi railway. In summer 1940, at the beginning of the Second World War, the line was extended by the Italian army by about 150 km: the railway reached Ferfer, near the present-day Somalia-Ethiopia border.[6]
- Genale–Afgoi (Italian Somalia). In 1924, a minor railway was built in the area just west of Italian Mogadishu and it had a small track in 600 mm gauge: the Genale-Afgoi decauville. The little railway was 46 km long and united the farming settlement of Genale with Afgoi on the Mogadishu-Villagio Duca degli Abruzzi route. Construction was managed by the "Società Agricola Italo Somala" (SAIS), which opened the track so that its plantations' powered sugar cane could be transported to the Mogadishu Port.
References
- Astuto 1941, p. 30.
- S. Maggi:"Le Ferrovie nell'Africa italiana"; p.23
- Gatti; p.21
- Astuto, Riccardo; p.34
- Astuto, Riccrdo; p.45
- Maggi; p.9
Bibliography
- Astuto, Riccardo (1941). "Questioni ferroviarie africane". Rassegna Economica dell'Africa Italiana. Roma. XXIX.
- Basuyau, Vincent (1991). Le chemin de fer de Djibouti à Addis Abeba (Mémoire de DEA). Paris: Université de Paris I-Panthéon Sorbonne.
- Crozet, Jean Pierre. "The Franco Ethiopian and Djibouto Ethiopian railway". Missing or empty
|url=(help) Detailed Website on the Addis Abeba-Djibouti railway - Gatti, G. (1975). Le ferrovie coloniali italiane. Roma: Ed. GRAF.