Isoserine
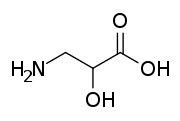
Isoserine is a non-proteinogenic α-hydroxy-β-amino acid, and an isomer of serine. Non-proteinogenic amino acids do not form proteins, and are not part of the genetic code of any known organism. Isoserine has only been produced synthetically.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Amino-2-hydroxypropanoic acid | |
| Other names
3-Aminolactic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 105.093 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The first documented synthesis of isoserine in a laboratory setting was by Miyazawa et al., who published their results in 1976.[1]
See also
References
- Ziora, Zyta; Skwarcynski, Mariusz; Kiso, Yoshiaki (2011). "Medicinal Chemistry of α-Hydroxy-β-Amino Acids". In Hughes, Andrew B. (ed.). Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins in Organic Chemistry, Volume 4: Protection, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, Combinatorial Synthesis. Wiley-VCH. Section 6.2.2: Synthesis of α-Hydroxy-β-amino acids. ISBN 978-3-527-63182-7. OCLC 741558720. Retrieved 2017-06-10 – via Google Books.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.