Iodophenol
Iodophenol is a substitution product of phenol in which one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by iodine.[1]
| Iodophenols | |||
| Name | 2-Iodophenol | 3-Iodophenol | 4-Iodophenol |
| Other names | o-Iodophenol | m-Iodophenol | p-Iodophenol |
| Chemical structure | 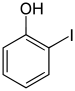 |
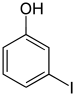 |
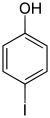 |
| CAS number | 533-58-4 | 626-02-8 | 540-38-5 |
| PubChem | CID 10784 from PubChem | CID 12272 from PubChem | CID 10894 from PubChem |
| Molecular formula | C6H5IO | ||
| Molar mass | 220.01 g/mol | ||
| Physical state | Solid | ||
| Melting point | 43 °C[2] | 40 °C[2] | 92–94 °C[2] |
| Boiling point | 186–187 °C (160 Torr)[2] |
||
| pKa[2] | 8.46 | 9.17 | 9.20 |
| GHS hazard pictograms |  [3] [3] |
 [4] [4] |
  [5] [5] |
| GHS hazard statements | H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | H315, H319, H335 | H302, H312, H314 |
| P261, P280, P305+351+338 | P261, P305+351+338 | P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |
References
- Karrer, Paul, Organic Chemistry, Elsevier Publishing Company, 1947, page 434.
- Rappoport (1984). CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification (3rd ed.). ISBN 0-8493-0303-6.
- "2-Iodophenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
- "3-Iodophenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
- "4-Iodophenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.