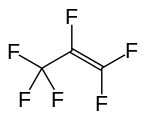
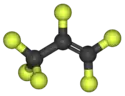
Hexafluoropropylene
Hexafluoropropylene is a synthetic alkene with the formula C3F6. It is the perfluorocarbon counterpart to the hydrocarbon propylene.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hexafluoropropene | |||
| Other names
Perfluoropropene, Perfluoropropylene, freon R 1216, halocarbon R 1216, fluorocarbon 1216 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.753 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1858 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3F6 | |||
| Molar mass | 150.023 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, odorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.332 g/ml, liquid at 20 °C | ||
| Melting point | −153 °C (−243 °F; 120 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −28 °C (−18 °F; 245 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Suffocation | ||
| GHS pictograms |    | ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H280, H332, H335, H351, H371, H373 | |||
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P281, P304+312, P304+340, P308+313, P309+311, P312, P314, P403+233, P405, P410+403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non flammable gas | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkenes; organofluorides |
propylene; Hexafluoroacetone, Hexafluoro-2-propanol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Hexafluoropropylene is used as a chemical intermediate.[1] It is often used a copolymer[2] in fluoroplastics such as fluorinated ethylene propylene.
Hexafluoropropylene can be produced by pyrolysis of tetrafluoroethylene or chlorodifluoromethane, or produced from various chlorofluorocarbons.[3]
This gas can also be produced as an effluent from the decomposition of polytetrafluoroethylene when laser cutting it. [4]
Health Effects
Hexafluoropropylene can asphyxiate by the displacement of air.[2]
References
- Lehmler, HJ (March 2005). "Synthesis of environmentally relevant fluorinated surfactants—a review". Chemosphere. 58 (11): 1471–96. Bibcode:2005Chmsp..58.1471L. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.078. PMID 15694468.
- "Hexafluoropropene (compound)". PubChem. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- United States patent (expires 5-20-2020) 5043491A, James L. Webster, Elrey L. McCann, Douglas W. Bruhnke, Jan J. Lerou, "Multistep synthesis of hexafluoropropylene", published 1991-08-27, issued 1991-08-27, assigned to E. I. Du Pont de Nemours and Company
- "Laser cutting teflon". Universal Laser Systems, Inc.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.