Gould's sequence
Gould's sequence is an integer sequence named after Henry W. Gould that counts the odd numbers in each row of Pascal's triangle. It consists only of powers of two, and begins:[1][2]
- 1, 2, 2, 4, 2, 4, 4, 8, 2, 4, 4, 8, 4, 8, 8, 16, 2, 4, 4, 8, 4, 8, 8, 16, 4, 8, 8, 16, 8, 16, 16, 32, ... (sequence A001316 in the OEIS)
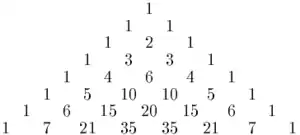
For instance, the sixth number in the sequence is 4, because there are four odd numbers in the sixth row of Pascal's triangle (the four bold numbers in the sequence 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1).
Additional interpretations
The nth value in the sequence (starting from n = 0) gives the highest power of 2 that divides the central binomial coefficient , and it gives the numerator of (expressed as a fraction in lowest terms).[1]

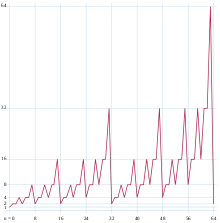
Gould's sequence also gives the number of live cells in the nth generation of the Rule 90 cellular automaton starting from a single live cell.[1][3] It has a characteristic growing sawtooth shape that can be used to recognize physical processes that behave similarly to Rule 90.[4]
Related sequences
The binary logarithms (exponents in the powers of two) of Gould's sequence themselves form an integer sequence,
- 0, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 1, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, ... (sequence A000120 in the OEIS)
in which the nth value gives the number of nonzero bits in the binary representation of the number n, sometimes written in mathematical notation as .[1][2] Equivalently, the nth value in Gould's sequence is
Taking the sequence of exponents modulo two gives the Thue–Morse sequence.[5]
The partial sums of Gould's sequence,
- 0, 1, 3, 5, 9, 11, 15, 19, 27, 29, 33, 37, 45, 49, 57, 65, 81, 83, 87, 91, 99, 103, 111, ... (sequence A006046 in the OEIS)
count all odd numbers in the first n rows of Pascal's triangle. These numbers grow proportionally to , but with a constant of proportionality that oscillates between 0.812556... and 1, periodically as a function of log n.[6][7]
Recursive construction and self-similarity
The first 2i values in Gould's sequence may be constructed by recursively constructing the first 2i − 1 values, and then concatenating the doubles of the first 2i − 1 values. For instance, concatenating the first four values 1, 2, 2, 4 with their doubles 2, 4, 4, 8 produces the first eight values. Because of this doubling construction, the first occurrence of each power of two 2i in this sequence is at position 2i − 1.[1]
Gould's sequence, the sequence of its exponents, and the Thue–Morse sequence are all self-similar: they have the property that the subsequence of values at even positions in the whole sequence equals the original sequence, a property they also share with some other sequences such as Stern's diatomic sequence.[3][8][9] In Gould's sequence, the values at odd positions are double their predecessors, while in the sequence of exponents, the values at odd positions are one plus their predecessors.
History
The sequence is named after Henry W. Gould, who studied it in the early 1960s. However, the fact that these numbers are powers of two, with the exponent of the nth number equal to the number of ones in the binary representation of n, was already known to J. W. L. Glaisher in 1899.[10][11]
Proving that the numbers in Gould's sequence are powers of two was given as a problem in the 1956 William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition.[12]
References
- Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A001316 (Gould's sequence)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- Pólya, George; Tarjan, Robert E.; Woods, Donald R. (2009), Notes on Introductory Combinatorics, Progress in Computer Science and Applied Logic, 4, Springer, p. 21, ISBN 9780817649531.
- Wolfram, Stephen (1984), "Geometry of binomial coefficients", American Mathematical Monthly, 91 (9): 566–571, doi:10.2307/2323743, MR 0764797.
- Claussen, Jens Christian; Nagler, Jan; Schuster, Heinz Georg (2004), "Sierpinski signal generates 1∕f α spectra", Physical Review E, 70: 032101, arXiv:cond-mat/0308277, Bibcode:2004PhRvE..70c2101C, doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.70.032101.
- Northshield, Sam (2010), "Sums across Pascal's triangle mod 2", Congressus Numerantium, 200: 35–52, MR 2597704, archived from the original on 2015-09-10, retrieved 2016-09-10.
- Harborth, Heiko (1976), "Number of odd binomial coefficients", Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 62 (1): 19–22, doi:10.2307/2041936, MR 0429714.
- Larcher, G. (1996), "On the number of odd binomial coefficients", Acta Mathematica Hungarica, 71 (3): 183–203, doi:10.1007/BF00052108, MR 1397551.
- Gilleland, Michael, Some Self-Similar Integer Sequences, OEIS, retrieved 2016-09-10.
- Schroeder, Manfred (1996), "Fractals in Music", in Pickover, Clifford A. (ed.), Fractal Horizons, New York: St. Martin's Press, pp. 207–223. As cited by Gilleland.
- Granville, Andrew (1992), "Zaphod Beeblebrox's brain and the fifty-ninth row of Pascal's triangle", American Mathematical Monthly, 99 (4): 318–331, doi:10.2307/2324898, MR 1157222.
- Glaisher, J. W. L. (1899), "On the residue of a binomial-theorem coefficient with respect to a prime modulus", The Quarterly Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 30: 150–156. See in particular the final paragraph of p. 156.
- Gleason, Andrew M.; Greenwood, R. E.; Kelly, Leroy Milton, eds. (1980), The William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition: Problems and Solutions: 1938–1964, Mathematical Association of America, p. 46, ISBN 9780883854624.