Fouquieria splendens
Fouquieria splendens (commonly known as ocotillo American Spanish: [okoˈtiʝo], but also referred to as coachwhip, candlewood, slimwood, desert coral, Jacob's staff, Jacob cactus, and vine cactus) is a plant indigenous to the Sonoran Desert and Chihuahuan Desert in the Southwestern United States (southern California, southern Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas), and northern Mexico (as far south as Hidalgo and Guerrero).[2][3]
| Fouquieria splendens | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ocotillo near Gila Bend, Arizona | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Fouquieriaceae |
| Genus: | Fouquieria |
| Species: | F. splendens |
| Binomial name | |
| Fouquieria splendens | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Fouquieria spinosa Torr. | |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fouquieria splendens. |
While semi-succulent and a desert plant, Ocotillo is more closely related to tea and blueberries than to cactuses. For much of the year, the plant appears to be an arrangement of large spiny dead sticks, although closer examination reveals that the stems are partly green. With rainfall, the plant quickly becomes lush with small (2–4 cm), ovate leaves, which may remain for weeks or even months.
Individual stems may reach a diameter of 5 cm at the base, and the plant may grow to a height of 10 m (33 ft). The plant branches very heavily at its base, but above that, the branches are pole-like and rarely divide further. Specimens in cultivation may not exhibit any secondary branches. The leaf stalks harden into blunt spines, and new leaves sprout from the base of the spine.
The bright crimson flowers appear especially after rainfall in spring, summer, and occasionally fall. Flowers are clustered indeterminately at the tips of each mature stem. Individual flowers are mildly zygomorphic and are pollinated by hummingbirds and native carpenter bees.
Distribution
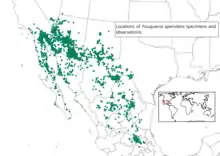
Ocotillo occurs in desert regions of southwestern United States thru central Mexico. It grows in dry, generally rocky soils.[4]
Cultivation

Ocotillo can be planted year-round with care. Ideal plants have been grown in pots from stem cuttings and from seed. Transplanting large bare-root plants has marginal success. They should be planted to the original growing depth and, as with cacti, in their original directional orientation: the original south side of the plant, which has become more heat- and sunlight-resistant, should again face the brighter, hotter southern direction. If their direction is not marked, success is again limited.
Uses
- Individual ocotillo stems are sometimes used as poles as a fencing material in their native region, and often take root to form a living fence.
- Due to their light weight and interesting pattern, ocotillo branches have been used for canes or walking sticks.
- Fresh flowers are sometimes used in salads and have a tangy flavor.
- Flowers are collected, dried, and used for tisanes.
- According to Medicinal Plants of the Desert and Canyon West (a book published in 1989 by Museum of New Mexico Press), a fresh bark tincture can be made by chopping or snipping freshly removed bark into 1/2-inch pieces. It is said to be useful for those symptoms that arise due to fluid congestion and to be absorbed from the intestines into the mesenteric lymph system by way of the lacteals of the small intestinal lining. This is believed to stimulate better visceral lymph drainage into the thoracic duct and improve dietary fat absorption into the lymph system.[5]
- Bathing in water that contains crushed flowers or roots has been used to relieve fatigue.[5]
- Native Americans place the flowers and roots of ocotillo over fresh wounds to slow bleeding.[5]
- Ocotillo is also used to alleviate coughing, achy limbs, varicose veins, urinary tract infections, cervical varicosities, and benign prostate growths.[5]
Subspecies
The three subspecies are:
Gallery
 An ocotillo flower with visible needles
An ocotillo flower with visible needles Ocotillo forest in the Santa Rita Mountains of Arizona
Ocotillo forest in the Santa Rita Mountains of Arizona Closeup of ocotillo leaves
Closeup of ocotillo leaves Closeup of ocotillo thorns in Anza-Borrego Desert State Park
Closeup of ocotillo thorns in Anza-Borrego Desert State Park Closeup of ocotillo flowers in Anza-Borrego Desert State Park
Closeup of ocotillo flowers in Anza-Borrego Desert State Park Ocotillo covered with rare snow in Tucson, Arizona
Ocotillo covered with rare snow in Tucson, Arizona Ocotillo in full bloom near Lookout Mountain, Phoenix, Arizona
Ocotillo in full bloom near Lookout Mountain, Phoenix, Arizona Ocotillo flower with a bee above — Tucson
Ocotillo flower with a bee above — Tucson Ocotillo with leaves outside Tucson Mountains after a rainfall event
Ocotillo with leaves outside Tucson Mountains after a rainfall event Ocotillo plant in Joshua Tree National Park
Ocotillo plant in Joshua Tree National Park
References
- The Plant List, Fouquieria splendens Engelm.
- Biota of North America Program 2014 county distribution map
- McVaugh, R. 2001. Ochnaceae to Loasaceae. 3: 9–751. In R. McVaugh (ed.) Flora Novo-Galiciana. The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
- Schultheis, Lisa M.; Stone, William J. (2012). "Fouquieria splendens subsp. splendens". Jepson eFlora. Retrieved January 10, 2021.
- Maya Strunk (Spring 2001 Independent study) at Medicinal Plants of the Southwest