Fluorophosphoric acid
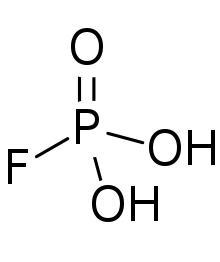
Fluorophosphoric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2PO3F. It is a colorless viscous liquid that solidified to a glass upon cooling.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Fluorophosphonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.202.790 |
| EC Number |
|
| 100863 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FH2O3P | |
| Molar mass | 99.985 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.818 g/cm3 |
| yes | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes skin burns and eye damage. |
| GHS pictograms | 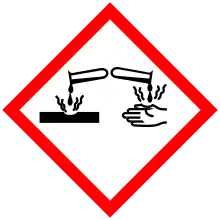  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H314, H330 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+310, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fluorophosphoric acid is produced by treating phosphorus pentoxide with hydrogen fluoride. It can also be prepared by hydrolysis of phosphorus oxyfluoride.[1] The reaction first produces difluorophosphoric acid:
- POF3 + H2O → HPO2F2 + HF
The next steps give monofluorophosphoric acid:
- HPO2F2 + H2O → H2PO3F + HF
Complete hydrolysis gives phosphoric acid:
- H2PO3F + H2O → H3PO4 + HF
Reactions
Fluorophosphoric acid is a dibasic acid, with pKas of 3.5 and around 8.5. The conjugate bases are the monofluorophosphates, which are hydrolytically robust.
References
- Charles B. Lindahl, Tariq Mahmood (2000). "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic, Phosphorus". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1608151912091404.a01. ISBN 9780471484943.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Phosphoryl fluoride. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.