Fluopyram
Fluopyram is a fungicide used against fungal diseases such as gray mold (Botrytis), powdery mildew, apple scab, Alternaria, Sclerotinia, and Monilinia. It is an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase.[2]
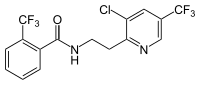 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-{2-[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]ethyl}-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.127.749 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11ClF6N2O | |
| Molar mass | 396.72 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 117.5 °C (243.5 °F; 390.6 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 318–321 °C (604–610 °F; 591–594 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In 2012, it was approved by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency[2] and in 2013 it was approved in the EU for use as an active ingredient in pesticides.[3]
References
- "Fluopyram" (PDF). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- "Fluopyram". New Active Ingredient Review. Minnesota Department of Agriculture. April 2012. Archived from the original on 2017-04-26. Retrieved 2015-09-16.
- "DURCHFÜHRUNGSVERORDNUNG (EU) Nr. 802/2013 DER KOMMISSION" (in German). August 2013. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.