Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe
The Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe was a high-wing, cantilever type, prototype experimental airplane produced in 1935.[1][2][3]
| SF-2 Plymocoupe | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe | |
| Role | Light aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Fahlin Aircraft Company |
| Designer | Swen Swanson, Ole Fahlin |
| First flight | 1935 |
| Introduction | 1935 |
| Status | Single prototype destroyed in hangar fire in 1938 |
| Primary users | Fahlin Aircraft Company Russel Owen |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
The SF-2, designed in response to a competition called by the United States Bureau of Air Commerce seeking design and construction proposals for an airplane affordable to the masses, was designed and built by Ole Fahlin and his partner Swen Swanson using the engine of a 1935 Plymouth automobile and featuring design accents, both interior and exterior, borrowed from the same car.[3][4][5][6]
The Plymocoupe, classified as a "flying automobile", utilised the engine, dashboard, indicators and hood ornament of the 1935 Plymouth car.[4][7][8]
History
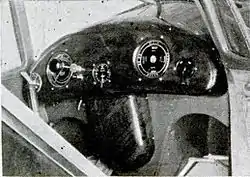
Based on the Swanson-Fahlin SF-1, Fahlin used a regular six-cylinder in-line Chrysler car engine, adapted to aircraft use, to power the airplane, supported by rubber suspension.[2][7][8][9][10] The SF-2 was flight tested by the Bureau of Commerce, but failed to meet the specifications of the contest contract.
Engine conversion
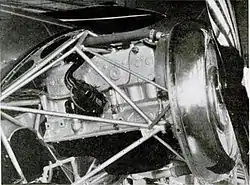
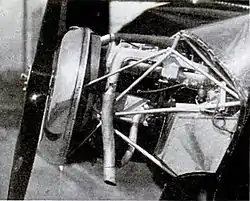
The stock Chrysler engine was modified for aeronautics use by removing the flywheel and cooling fan. The automotive electrical ignition system was replaced by an air plane magneto and a new lighter exhaust system was installed. The standard carburetor was replaced by the updraught type where the air entered from below and exited at the top of the unit. The cylinder heads were replaced by new ones made from aluminium which had the effect of decreasing the weight of the engine while increasing the compression ratio from 6.7:1 to 7:1.[8] The reduction gearbox was mounted on the engine housing directly connected to the crankshaft, lubricated by the engine oil system.[8]

The propeller was driven via the gearbox using a 2:1 gear-reduction ratio, which enabled the engine to operate at full power driving the propeller at its optimum speed of 1800 rpm.[7][8] The propeller shaft passed through the radiator, which was mounted in front of the engine.[7]
Most engine parts remained stock and could be obtained at any of the approximately 8,000 Chrysler, De Soto or Dodge dealers in the United States, while any engine repairs and maintenance could be performed by any Chrysler-trained mechanic.[7] Among design accents reminiscent of automotive design, the aircraft cowling featured portholes similar to the ones found in the original 1935 Plymouth car.[8] Other features included mohair interior, adjustable windows and a cowling ornament in the form of a ship,[6][11] similar to the hood ornament of the car.[7] Flying magazine praised Fahlin's engine conversion to aircraft use as "one of the smoothest jobs of adapting an automobile motor to aircraft use".[7]
Engine certification
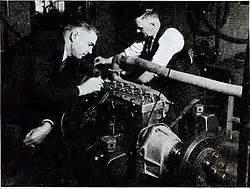
The SF-2 engine was required to pass two series of tests before being granted the ATC (Approved Type Certificate) which would allow it to be used in aircraft flight applications. The regulations required a government-run 50-hour test on the Chrysler engine and an additional 100-hour test undertaken by the manufacturer itself. Chrysler was willing at the time to participate in the process because it forecast increased demand for aviation-related applications of its automobile engines. The engine passed all necessary tests. At the same time the Bureau of Air Commerce asked Fahlin Aircraft Company in Marshall, MO to manufacture an airplane which would be used to test the certified engine in flight.[8]
Wings

An innovative feature of the wing arrangement was that the flaps could also be used as ailerons in a configuration akin to a flaperon. The flap area was one third of the total wing area and the flaps extended along the entire length of the wing. A lever controlled the flap action and through a different configuration it could change to aileron control mode.[7]
Landing gear
The landing gear provided knee-action struts for absorbing the shock during landing.[7]
Operational history
Flight tests

During flight tests the Plymocoupe achieved a maximum speed of 120 mph (190 km/h; 100 kn) and cruising speed of 100 mph (160 km/h; 87 kn). On a trip between two cities in the midwest of the United States it took the airplane two and a half hours to cover a distance of 250 mi (400 km; 220 nmi). The engine used standard gasoline and its fuel consumption was 25 mpg‑US (9.4 L/100 km; 30 mpg‑imp), while its oil consumption for the trip was approximately a quart.[8] Its performance was superior to the similarly powered Porterfield 35, in all aspects except during takeoff.[10]
Attempted non-stop flight

The aircraft was tested and certified as airworthy and Fahlin was commissioned by Chrysler to bring it to Detroit for additional tests. However the failure of the SF-2 to win the competition and the death of Fahlin's partner Swanson, from pneumonia, led to the sale of the aircraft to Russel Owen, who was planning a non-stop flight from Anchorage to Seattle. The aircraft was subsequently renamed Sea-Aska and modified by increasing its fuel capacity.[6][12]
At the time, the Anchorage Daily Times had written that the flight would set a record for "the longest flight ever made with an automobile engine."[11] The aircraft had the name Se As Ka at the pilot door followed by the description "The Flying Automobile", while the side of the fuselage was inscribed by the message "Seattle-Alaska Last Airmail Frontier Trail Blazed by The Seattle Washingtonians".[5][13]
However while flying over Juneau in fog, on 28 September 1936,[14] Owen thought that he had oil-pressure problems and crash-landed near the unlit Juneau airport at night.[5][6][12] In September 1936, following the crash-landing, Owen sent a telegram to his sponsors writing: "Sea-Aska on her asska in Alaska."[15][16][17][18] The landing gear of the airplane failed and there was damage to the cowling and the propeller.[19] The aircraft remained un-repaired in Shell Simmons' hangar at Juneau airport until 1938 when it burned during a hangar fire, started accidentally by technicians working in the hangar.[14][15][18]
Specifications (SF-2)
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Capacity: one passenger or 536 lb (243 kg) useful load
- Length: 17 ft 8 in (5.38 m)
- Wingspan: 32 ft (9.8 m)
- Wing area: 178 sq ft (16.5 m2)
- Empty weight: 1,075 lb (488 kg)
- Gross weight: 1,611 lb (731 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 17 US gal (64 l; 14 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 1 × Plymouth 6-cyl water-cooled in-line piston engine, 80 hp (60 kW) with 2:1 reduction gearing
Performance
- Maximum speed: 120 mph (190 km/h, 100 kn)
- Cruise speed: 104 mph (167 km/h, 90 kn)
- Endurance: 5 hours
- Service ceiling: 16,000 ft (4,900 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,000 ft/min (5.1 m/s) solo
- Wing loading: 9.04 lb/sq ft (44.1 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.0476 hp/lb (0.0782 kW/kg)
References
- AAHS Journal. 51. American Aviation Historical Society. 2006. p. 14.
- Frederick Thomas Jane (1935). Jane's All the World's Aircraft. S. Low, Marston Limited. p. 261.
The Fahlln "Plymo-coupe" Two-seat Cabin Monoplane (80 h.p. "Plymouth" engine). ... THE FAHLIN "PLYMO-COUPE" S.F.II. Type. ... One 80 h.p. Plymouth six-cylinder in-line upright water-cooled converted automobile engine. Frontal radiator. [...] The Chrysler Company are applying for a Department of Commerce Approved Type Certificate for the "Plymouth" engine. THE FAHLIN "PLYMO-COUPE" S.F.II. Type. — Two-scat light cabin monoplane. Winus. High-wing cantilever monoplane ...[...]... of Mr. Sven Swanson. formerly President and Chief Engineer of the Swanson Aircraft Co., Inc., with the Ho h.p. Pobjoy "R" engine. This machine was the prototype of the Fahlin "Plymocoupe," which is described under "Fahlin. ...
- AAHS Journal. American Aviation Historical Society. 1999. pp. 120–122.
The Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe was also built and tested by the Bureau in the program but was apparently rejected as unsuitable.[...] Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe (1935)
- George W. Green (30 June 2010). Flying Cars, Amphibious Vehicles and Other Dual Mode Transports: An Illustrated Worldwide History. McFarland. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-7864-4556-1.
Now, turning to that strange phenomenon, an airplane that thinks it's a car, we run into the Plymocoupe Airplane which sported the portholes and side trim of the 1935 Plymouth. It was labeled a flying automobile because it was powered by an engine manufactured for use in a 1935 Plymouth.
- Sport Aviation. 42. 1993. pp. 172–173.
Damage to Owen's aircraft of many names - variously known as the SF- 2, Plymocoupe (also Plymacoupe and ... Ole Fahlin, known for his propeller designs, and airplane designer Swen Swanson teamed up in planning the airplane for Fahlin ...[...] Regardless, the Anchorage-Seattle non-stop trip would be "the longest flight ever made with an automobile engine," ... (with slash marks indicating line breaks): "Se- As'Ka/The Flying Automobile" and "Seattle-Alaska/Last Airmail Frontier/Trail ...[...] Pilot Russell Owen took off from Anchorage on Sept. 28, 1936, in hopes of making a non-stop flight to Seattle to promote an Anchorage- Seattle airmail route. He crashed during an emergency night landing at an unlighted airport near Juneau.
- Kimes, Beverly Rae; Clark, Henry Austin, Jr. (2 September 1996). Standard Catalog of American Cars 1805-1942. Krause Publications. p. 1206. ISBN 978-0-87341-428-9.
Ole Fahlin and Swen Swanson built an experimental airplane powered by a 1 935 Plymouth engine converted for aviation use to ... When the Fahlm- Swanson design (called the Plymocoupe or SF-2) failed to win the government contest and... [...] on its Plymouth heritage the plane also used the 1935 hood trim on the cowling, a "sailing ship" radiator ornament on the ...
- Flying Magazine. August 1935. p. 96. ISSN 0015-4806.
Here is a Plymouth Sedan and its offspring, the flying Plymo-Coupe. Many Plymouth auto parts are used in the plane. Right side of the Plymo-Coupe power plant showing that all.
- Flying Magazine. October 1935. p. 237. ISSN 0015-4806.
- American Aviation Historical Society (1965). American Aviation Historical Society Journal. American Aviation Historical Society.
The complete unit, including water in the radiator, weighed 502 lbs. it developed 82 hp at 1550 RPM (prop speed) for takeoff and was not inverted, as the photos clearly show. Walt Chrysler was interested and conducted 100 hour tests for ...
- American Aviation Historical Society (1965). American Aviation Historical Society Journal. American Aviation Historical Society. p. 295.
despite the engine weight penalty. Except for the initial takeoff, it outperformed a Porterfield of the same horsepower.
- Sport Aviation. 42. 1993. p. 173.
Regardless, the Anchorage-Seattle non-stop trip would be "the longest flight ever made with an automobile engine," claimed the Anchorage Daily Times.[...] To further suggest its origins, the Plymocoupe sported the portholes and side trim of the 1 935 Plymouth and used, in modified form, some of the Plymouth gauges. A 1935 Plymouth ship ornament was perched on the nose of the plane.
- Stephen E. Mills (1971). Arctic war birds: Alaska aviation of WWII. Superior Pub. Co. p. 31.
Fahlin Plymocoupe, dubbed "Seaska," crash-landed short of the Juneau airport when enterprising pilot-owner Russ Owen thought he had lost the oil pressure in the aircraft's 1935 Plymouth engine. Owen promoted ...
- "Museum of History and Industry Images". Museum of History and Industry, Seattle. Archived from the original on 2013-12-30.
- "Vintage Airplane" (PDF). 21 (9). 1993: 7–8. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Swanson-Fahlin SF-2 Finis [365]".
- AAHS Journal. 28. The Society. 1983. p. 247.
The airplane had been named SEA ASKA. When Owens wired his backers of the flight's termination his telegram read, "Sea- ska on her Asska in Alaska." The aircraft was I in a hangar in Juneau until destroyed by 1 1 938. (Photo by Lloyd ..
- Sport Aviation. 1993. pp. 172–175.
He took off again from Anchorage's Merrill Field at 9:15 a.m. on September 28, after a five-hour wait for fog to clear. ... The plane lumbered down the runway after Owen received weather reports "showing conditions favorable all the way ... "Crash Wrecks Se-As-Ka, Owen Unhurt," read the Anchorage Times' headline over a September 29th Associated Press article from Juneau. The pilot, wedged into a tiny space amidst gasoline tanks, was unable to free himself and was compelled to remain in an ... Pilots pointed out that a spark could have ignited the plane and turned it into a blazing tomb for the aviator who was ... The telegram read: "'SE-AS-KA' on her 'ASKA' in Alaska.
- James Benjaminson. "The Flying Plymouth". allpar.com.
To the Washingtonians awaiting his arrival in Seattle, Owen sent a telegram reading simply "Se-As-Ka on her 'aska' in Alaska".
- Sport Aviation. 1993. pp. 173–175.
Damage to Owen's plane of many names - variously known as the SF- 2, Plymocoupe (also Plymacoupe and Plymo-Coupe), the Flying Automobile, and Se-As-Ka - included a splintered propeller, crumpled cowling and collapsed landing gear ...