Ellsworth Mountains
The Ellsworth Mountains are the highest mountain ranges in Antarctica, forming a 350 km (217 mi) long and 48 km (30 mi) wide chain of mountains in a north to south configuration on the western margin of the Ronne Ice Shelf in Marie Byrd Land. They are bisected by Minnesota Glacier to form the Sentinel Range to the north and the Heritage Range to the south. The former is by far the higher and more spectacular with Mount Vinson (4,892 meters (16,050 ft)) constituting the highest point on the continent.[1][2] The mountains are located within the Chilean Antarctic territorial claim but outside of the Argentinian and British ones.
| Ellsworth Mountains | |
|---|---|
 The central part of Ellsworth Mountains with Mount Tyree, Mount Shinn and Mount Vinson; Nimitz Glacier in the foreground | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Vinson |
| Elevation | 4,892 m (16,050 ft) |
| Coordinates | 78°31′31.74″S 85°37′01.73″W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 360 km (220 mi) NNW-SSE |
| Width | 48 km (30 mi) WE |
| Geography | |
 Location of Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica | |
| Continent | Antarctica |
| Region | Ellsworth Land |
| Range coordinates | 78°45′S 85°00′W [1] |
Discovery
The mountains were discovered on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth in the course of a trans-Antarctic flight from Dundee Island to the Ross Ice Shelf. He gave them the descriptive name Sentinel Range.[1]
The mountains were mapped in detail by the U.S. Geological Survey from ground surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1958–66. When it became evident that the mountains comprise two distinct ranges, the US-ACAN restricted the application of Sentinel Range to the high northern one and gave the name Heritage Range to the southern one; the Committee recommended the name of the discoverer for this entire group of mountains.[1]
Geology
Geologically, the Ellsworth Mountains occupy a discrete block of continental crust known as the Ellsworth-Whitmore Mountain terrane. This terrane was part of the early Paleozoic amalgamation of Gondwana and consists of a 13,000 meters (43,000 ft) thick section of folded Cambrian–Permian strata, which accumulated on Grenville-age continental crust. It was likely was once part of the Cape Fold Belt that was detached from southern Africa during the breakup of Gondwana and later incorporated into Antarctica.[3][4]
The stratigraphy consists of the 7,500 meters (24,600 ft) thick Early Cambrian-Middle Cambrian Heritage Group, overlain by the 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) thick Late Cambrian-Devonian Crashsite Group, the 1,000 meters (3,300 ft) thick Permo-Carboniferous Whiteout Conglomerate black diamictite from Gondawanaland glaciation, and the 1,000 meters (3,300 ft) thick Permian Polarstar Formation consisting of black argillite, siltstone, sandstone, and coal. Within the Heritage Group is the Union Glacier Formation of ashflow tuff-lahar deposits, the Hyde Glacier Formation of graywacke-argillite-conglomerate, the Drake Icefall Formation of black shales and marble, the Conglomerate Ridge Formation of conglomerate and quartzite, the Liberty Hills-Springer Peak-Frazier Ridge Formations of quartzite-argillite, and the Minaret Formation of marble. Within the Crashsite Group is the Howard Nunataks Formation of quartzites, the Mt. Liptak Formation of quartzites, and the Mount Wyatt Earp Formation of quartzites. Major deformation of the sedimentary rocks occurred during the Gondwanide orogeny, followed by later uplift.[3]
Climate
The temperatures in the Ellsworth Mountains average around -30 °C (-20 °F). The best time for expeditions are November through January, mid-summer in the Southern Hemisphere. However, arranging an outing here is a difficult task, requiring either official scientific sponsorship or considerable financial resources.
Maps
- Newcomer Glacier. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1961.
- Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988.
- Union Glacier. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1966.
- Liberty Hills. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1966.
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated.
Gallery
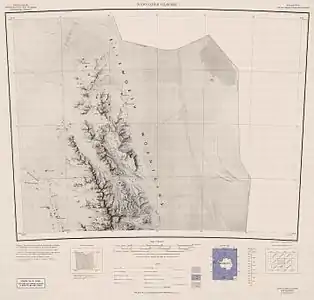 Northern Sentinel Range, USGS map
Northern Sentinel Range, USGS map Central and southern Sentinel Range, USGS map
Central and southern Sentinel Range, USGS map The central part of the mountains with Vinson Plateau, NASA satellite image
The central part of the mountains with Vinson Plateau, NASA satellite image Northern Heritage Range, USGS map
Northern Heritage Range, USGS map Southern Heritage Range, USGS map
Southern Heritage Range, USGS map.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)
_from_East_by_Christian_Stangl_(flickr).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
References
- "Ellsworth Mountains". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2004-05-06.
- Bockheim, J.G., Schaefer, C.E., 2015. Soils of Ellsworth Land, the Ellsworth Mountains. In: Bockheim, J.G. (Ed.), The Soils of Antarctica. World Soils Book Series, Springer, Switzerland, pp. 169–181.
- Webers, Gerald; Craddock, Campbell; Splettstoesser, John (1992). Webers, Gerald; Craddock, Campbell; Splettstoesser, John (eds.). Geologic history of the Ellsworth Mountains, West Antarctica, in Geology and Paleontology of the Ellsworth Mountains, West Antarctica. Boulder: Geological Society of America. pp. 1–8. ISBN 0813711703.
- Craddock, J.P., Schmitz, M.D., Crowley, J.L., Larocque, J., Pankhurst, R.J., Juda, N., Konstantinou, A. and Storey, B., 2017. Precise U-Pb zircon ages and geochemistry of Jurassic granites, Ellsworth-Whitmore terrane, central Antarctica. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 129(1-2), pp.118-136.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ellsworth Mountains. |
.svg.png.webp)