Egg drop syndrome
EDS '76 is one of the important viral diseases of birds, notably chickens, ducks, geese and swans. It is characterised by a sudden drop in production of eggs as well as its eggshell quality in apparent healthy laying birds.[1]

Previously, this disease was commonly named as merely "egg drop syndrome", however, it is now recommended that full name; egg drop syndrome '76 (EDS '76) should be used to distinguish the name discrepancy from the recently identified disease in ducks caused by a flavivirus, which is confusingly called "egg drop syndrome in ducks" or "duck egg drop syndrome".
Incidence
EDS '76 was first identified in Netherlands in 1974[2] and the virus was first isolated in Northern Ireland in 1976.[3] It became a problem in European countries such as Ireland, Holland, France, and the United Kingdom. Other places which have had outbreaks include India,[4] Bangladesh,[5]South America,[6] Indonesia,[7] Japan, and Africa.[8] Since then, EDS '76 has been recognised as a global threat for the breeding and laying companies.
Cause
EDS '76 is caused by double stranded-DNA virus, called Duck Atadenovirus A (formerly knows as Duck Adenovirus A). The diameter of the virus is between 70 and 80 nm by negative staining.[3]
The other name of this virus may include duck adenovirus 1 (DAdV-1), EDS '76 virus (EDSV) and adenovirus 127 (AV-127).[9]
Species Affected
The natural host of Duck atadenovirus A are wild and/or domestic waterfowls such as ducks and geese. However, the virus can also infect other bird species through contaminated vaccines,[3] and contaminated drinking water by droppings.[9]
Moreover, the virus become apparent and more susceptible in chickens of all ages and breeds, especially broilers and brown egg layers. The virus also causes symptoms in Japanese quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica) and turkeys.[10]
Transmission
Duck atadenovirus A can be transmitted vertically (from hens to chicks). The virus is often latent until the chicks reach maturity. Thereafter, the matured chickens begin to excrete virus and transmit through the eggs and droppings.
The virus is also transmitted horizontally between chickens. Mainly, it is seen in commercial egg layers whereby contaminated egg trays are often reused. The virus can survive both inside the eggs and on the eggshell. The virus can migrate from the eggshell to the tray and back to the other eggs placed in the same tray. Contaminated water supply with droppings and litters of the natural host contributes to the horizontal spread as well.[1]
Insect transmission is possible yet proven.[11]
Sign & Symptoms
The first sign of EDS '76 is usually the loss of colour pigment in the eggs, followed by the production of thin-shelled, soft-shelled and even shell-less eggs. The thin-shelled and shell-less eggs are so fragile and thus may get eaten by the chickens and get disregarded as litters. The shells may also be rough or chalky. Watery egg whites and a reduction in egg size may also happen as well.[12][13]
The affected chicken flocks show a failure to reach a peak egg production. The fall in egg production can be up to 40%. The affected chickens may show transient diarrhoea, anaemia, and loss of appetite. Increase in mortality is not observed.[9][14]
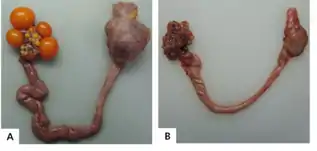
Lesions
The lesions are confined to female reproductive tracts. These may include inactive ovaries and shrunken oviducts, swelling and white exudate in the shell gland. Spleen enlargement may also be observed[9]
Diagnosis & Detection
EDS '76 can largely be distinguished from other poultry diseases, such as Avian Influenza, Infectious Bronchitis and Newcastle Disease, by the clinical findings alone. However, proper laboratory testing is still needed to eliminate doubts for a definitive diagnosis.[1]
Serological testing can determine if chicken have antibodies against EDS '76, which would indicate that they have been infected. This is only possible for non-vaccinated chickens because vaccination or infection both cause antibodies to be present. The common tests of choice include Haemaglutination-Inhibition, Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay and Serum Neutralisation.[15][16]
The use of sentinel birds (non-vaccinated susceptible birds) in the flocks is also useful for early detection and tested for haemagglutination. It is common practice for poultry viruses' surveillance.[17]
Identification of the virus can also be detected by Polymerase Chain Reaction-based test.[18]
Treatment and Prevention
There is no treatment for EDS '76, but there are ways in which chickens can be prevented form being infected by EDS '76.
Hygiene:
Cleaning all areas, such as breeding and laying areas, and equipment may mitigate the risk of getting EDS '76. Shared egg trays have to be cleaned and disinfected prior to use. Healthy and uninfected flocks should be kept away upon a contact with those affected birds and the virus natural host. Potential contaminated water should also be chlorinated.[1]
Vaccination:
An inactivated vaccine with oil adjuvant can be administered and has proven to be reasonably successful to prevent the clinical signs of the disease. This vaccine is given before hens start to lay eggs, usually between 14 and 20 weeks of age. Several vaccine are available: Izovac EDS, Nobilis EDS, AVIVAC-EDS-76 and other EDS '76 available vaccines.
References
- Smyth JA. "Overview of Egg Drop Syndrome in Poultry". Retrieved 20 February 2019.
- Van Eck JH, Davellaar FG, Meurelplerman TA, et al. (1976). "Dropped Egg Production, Soft Shelled and Shell-less Eggs Associated with Appearance of Precipitins to Adenovirus in Flocks of Laying Fowl". Avian Pathology. 5 (4): 261–272. doi:10.1080/03079457608418195. PMID 18777355.
- McFerran JB, McCracken RM, McKillop ER, et al. (1978). "Studies on a Depressed Egg Production Syndrome in Northern Ireland". Avian Pathology. 7 (1): 35–47. doi:10.1080/03079457808418258. PMID 18770358.
- Mohanty GC, Pradhan HK, Verma KC, et al. (1984). "Egg Drop Syndrome (EDS -'76) in India: Seroprevalence of EDS -'76 Virus Infections in Poultry Flocks". Indian Journal of Poultry Science. 19: 15–18.
- Biswas PK, Barua H, Uddin GM, Biswas D, Ahad A, Debnath NC (January 2009). "Serosurvey of five viruses in chickens on smallholdings in Bangladesh". Prev Vet Med. 88 (1): 67–71. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2008.06.018. PMID 18723236.
- Bishop SC, Cardozo, P (1996). "Egg Drop Syndrome '76 in Bolivia". Tropical Animal Health and Production. 28 (3): 199–206. doi:10.1007/BF02240935. PMID 8888524.
- Kencana GA, Suartha IN, Nurhandayani A, et al. (2017). "The Characteristic of Egg Drop Syndrome Virus of Medan Isolate" (PDF). Journal of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science. 1 (1): 15–19.
- Ezema WS, Nwanta J, Aka L, et al. (2010). "Egg-Drop Syndrome 76 in different bird species in Nigeria - A review of the epidemiology, economic losses, challenges and prospect for management and control". World's Poultry Science Journal. 66 (1): 115–122. doi:10.1017/S0043933910000115.
- Spickler, Rovid A (2017). "Egg Drop Syndrome 1976" (PDF). Retrieved 20 February 2019.
- Biđin Z, Lojkić I, Mikec M, et al. (2007). "Naturally Occurring Egg Drop Syndrome Infection in Turkeys". Acta Veterinaria Brno. 76 (3): 415–421. doi:10.2754/avb200776030415.
- OIE Report (2006). "Egg Drop Syndrome". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.180.4622. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Van Eck JH, Vertommen M, Van den HP, et al. (1977). "Recent studies on the role of adenovirus in the problem of dropped egg production and production of soft shelled and shell-less eggs". In Proc. Conf. On Avian Adenoviruses and Infectious Bronchitis: 42–44.
- Van Eck JH, Elanbass L, Wensvoort P, et al. (1978). "Histopathological changes in the oviduct of hens producing shell-less eggs associated with precipitins to adenovirus". Avian Pathology. 7 (2): 279–287. doi:10.1080/03079457808418279. PMID 18770379.
- Darbyshire JH, Peters RW (2007). "Studies on EDS‐76 virus infection in laying chickens". Avian Pathology. 9 (3): 277–290. doi:10.1080/03079458008418413. PMID 18770267.
- Adair BM, Todd D, McFerran JB, et al. (1986). "Comparative serological studies with egg drop syndrome virus". Avian Pathology. 15 (4): 677–685. doi:10.1080/03079458608436330. PMID 18766569.
- Volkova VA, Chvala IA, Mudrak NS (2016). "Evaluation of efficiency of ELISA for detection of antibodies to EDS-76 virus". Russian Veterinary Journal. Productive Animals. 2: 21–24.
- Poultry Health (December 2017). "Plan B: Using sentinel birds to track poultry viruses when you can't obtain SPF birds". Retrieved 20 February 2019.
- Zheney M, Kaziyev Z, Kassenova G, et al. (2018). "Real-time fluorescence loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for direct detection of egg drop syndrome virus". BMC Veterinary Research. 14 (1): 49. doi:10.1186/s12917-018-1364-9. PMC 5811957. PMID 29439721.