Diyala River
The Diyala River, is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjero river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of 445 km (277 mi).
| Diyala river | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Iraq |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | North of Iraq/Western Iran |
| Mouth | |
• location | Tigris River |
| Length | 445 km (277 mi) |
| Basin size | 32,600 km2 (12,600 sq mi)[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Sirwan |
| • right | Tanjero |
Course
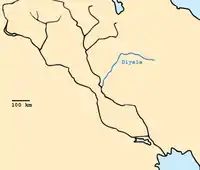
It rises near Hamadan, in the Zagros Mountains of Iran. It then descends through the mountains, where for some 32 km it forms the border between the two countries. It finally feeds into the Tigris below Baghdad. Navigation of the upper reaches of the Diyala is not possible because of its narrow defiles, but the river's valley provides an important trade route between Iran and Iraq.
The river flows southwest of the Hamrin Mountains.
Name
Its Aramaic origin is "Diyalas" and in Kurdish it is called "Sirwan", meaning 'roaring sea' or 'shouting river'. In early Islamic period, the lower course of the river formed part of the Nahrawan Canal. The Diyala Governorate in Iraq is named after the river.
History

The river is mentioned in Herodotus' Histories under the name Gyndes, where it is stated that the king Cyrus the Great dispersed it by digging 360 channels as punishment after a sacred white horse perished there. The river returned to its former proportions after the channels disappeared under the sand.
The Battle of Diyala River took place in 693 BC between the forces of the Assyrian empire and the Elamites of southern Iran.
In March 1917 the British Empire defeated the Ottoman Empire at the confluence with the Tigris, leading to the Fall of Baghdad, part of the Mesopotamian Campaign of World War I.
Archaeology
This area flourished already during the Jemdet Nasr and Early Dynastic periods, through to the Akkadian period. During the Larsa period, Eshnunna especially became prominent.
Major excavations were done in the lower Diyala river basin in the 1930s. They were conducted by the University of Chicago Oriental Institute (1930–1937) and by the University of Pennsylvania (1938–1939). The sites such as Tell Agrab, Tell Asmar (ancient Eshnunna), Ishchali (ancient Neribtum), and Khafaje (ancient Tutub) were excavated.
In Tell Asmar, the Tell Asmar Hoard is particularly notable. Twelve remarkable statues were found belonging to the Early Dynastic period (2900–2350 BC).
At that time, the Diyala was relatively unexplored compared to southern and northern Mesopotamia. But looting of sites was already underway. As the result, the professional excavations were launched.
Archaeologists James Breasted and Henri Frankfort were leading these projects.
These excavations provided very comprehensive data on Mesopotamian archaeology and chronology. They covered the time between the late Uruk period and the end of the Old Babylonian period (3000–1700 BC).
Subsequently, nine detailed monographs were published, but most of the objects, numbering 12,000, remained unpublished. Launched in 1992, the Diyala Database Project has been publishing a lot of this material.[2]
Other scholars who worked there were Thorkild Jacobsen as epigrapher, Seton Lloyd, and Pinhas Delougaz.[3]
More recently, the Diyala region was also explored intensively as part of the Hamrin Dam Salvage Project.[4]
The following sites were excavated from 1977 to 1981: Tell Yelkhi, Tell Hassan, Tell Abu Husaini, Tell Kesaran, Tell Harbud, Tell al-Sarah, and Tell Mahmud.[5]
Scarlet Ware

A type of pottery known as 'Scarlet Ware', a brightly coloured pottery with pictorial representations, was typical of sites along the Diyala River.[7] It developed around 2800 BC, and is related to the Jemdet Nasr ware in central Mesopotamia of the same period. The red colour was achieved predominantly by using haematite paint.
Scarlet Ware is typical of Early Dynastic I and II periods.[8] Along the Diyala is located one of the most important trade routes linking south Mesopotamia with the Iranian plateau. Thus, Scarlet ware was also popular in Pusht-i Kuh, Luristan, and it was traded to Susa during Susa II period.
Dams
In Iran the Daryan Dam is currently under construction near Daryan in Kermanshah Province. The purpose of the dam is to divert a significant portion of the river to Southwestern Iran for irrigation through the 48 km (30 mi) long Nosoud Water Conveyance Tunnel and to produce hydroelectric power.[9][10] In Iraq, the river first reaches the Darbandikhan Dam which generates hydroelectric power and stores water for irrigation. It then flows down to the Hemrin Dam for similar purposes. In the lower Diyala Valley near Baghdad the river is controlled by the Diyala Weir which controls floods and irrigates the area northeast of Baghdad.
- Darbandikhan Dam, Iraq
- Bawanur Dam (under construction), Iraq
- Hemrin Dam, Iraq
- Diyala Weir, Iraq
- Garan Dam, Iran
- Daryan Dam, Iran
 Lake Darbandikhan
Lake Darbandikhan Darbandikhan Dam
Darbandikhan Dam Diyala Weir
Diyala Weir
References
- Hussein, Haitham A. (June 2010). "Dependable Discharges of The Upper and Middle Diyala Basins". Journal of Engineering. 16 (2): 4960–4969. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- Diyala Project oi.uchicago.edu
- POTTERY FROM THE DIYALA REGION. By Pinhas Delougaz (The University of Chicago, Oriental Institute Publications, vol. LXIII). XXII+182 pp. +204 plates, Chicago 1952.
- McGuire Gibson (ed.), Uch Tepe I: Tell Razuk, Tell Ahmed al-Mughir, Tell Ajamat, Hamrin Reports 10, Copenhagen, 1981.
- IRAQ - Hamrin Centro Ricerche Archeologiche e Scavi di Torino per il Medio Oriente e l'Asia
- "Khafajeh jar". British Museum.
- Francesco Del Bravo, 'Scarlet Ware': Origins, Chronology and Developments, in M. Lebeau - P. de Miroschedji (eds), ARCANE Interregional Vol. I: Ceramics (ARCANE Interregional I), Turnhout (Brepols), 2014: 131-147
- Scarlet Ware jar britishmuseum.org
- "Darian Dam" (in Persian). Iran Water Resources Management. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- "Water Tunnel Nosoud" (in Persian). JTMA. Archived from the original on 23 January 2013. Retrieved 17 May 2013.