Diethyl dithiophosphoric acid
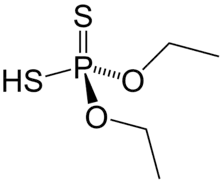
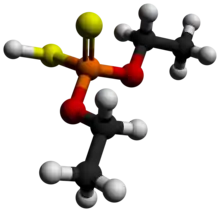
Diethyl dithiophosphoric acid, sometimes mistakenly called diethyl dithiophosphate, is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2PS2H. It is the processor for production of the organophosphate insecticide Terbufos. Although samples can appear dark, it is a colorless liquid.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diethoxy-sulfanyl-sulfanylidene-λ5-phosphane | |
| Other names
O,O-Diethyl dithiophosphoric acid; Diethyl dithiophosphate; Diethyl phosphorodithioate; Diethyl ester of phosphorodithioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.506 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11O2PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 186.22 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Melting point | < 0 °C (32 °F; 273 K) |
| Boiling point | 66 °C (151 °F; 339 K) at 1 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H314, H330 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+310, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 82 °C (180 °F; 355 K) |
| 538 °C (1,000 °F; 811 K) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
500 mg/kg (rabbit, dermal) 4510 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is prepared by treating phosphorus pentasulfide with ethanol:[2]
- P2S5 + 4 C2H5OH → 2 (C2H5O)2PS2H + H2S
Reactions
Diethyl- and dimethyl dithiophosphoric acids react with bases. The results of this neutralization reaction are salts, e.g., ammonium diethyl dithiophosphate.[3]
Diethyl dithiophosphoric acid reacts with zinc oxide to give zinc dithiophosphate, which is used as an oil additive:[4]
- ZnO + 2 (C2H5O)2PS2H → [(C2H5O)2PS2]2Zn + H2O
See also
References
- J. Svara, N. Weferling, T. Hofmann "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2
- Lefferts, J. L.; Molloy, K. C.; Zuckerman, J. J.; Haiduc, I.; Guta, C.; Ruse, D. (1980). "Oxy and thio phosphorus acid derivatives of tin. 1. Triorganotin(IV) dithiophosphate esters". Inorganic Chemistry. 19 (6): 1662–1670. doi:10.1021/ic50208a046.
- Okuniewski, Andrzej; Becker, Barbara (2011). "Ammonium O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphate". Acta Crystallogr. E. 67 (7): o1749–o1750. doi:10.1107/S1600536811022811. PMC 3151957. PMID 21837134.
- H. Spikes "The history and mechanisms of ZDDP" Tribology Letters, Vol. 17, No. 3, October 2004. doi:10.1023/B:TRIL.0000044495.26882.b5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

2.png.webp)