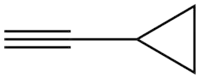
Cyclopropylacetylene
Cyclopropylacetylene is an hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C
5H
6.[2] Under normal conditions, the substance is a colorless liquid. Cyclopropylacetylene is a precursor pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ethynylcyclopropane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.389 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6 | |
| Molar mass | 66.103 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.781 g/cm3 at 25°C[1] |
| Boiling point | 51–53 °C (124–127 °F; 324–326 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| H225, H315, H319, H412 | |
| P210, P273, P280, P305+351+338 | |
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Several methods have been published on the synthesis of cyclopropylacetylene. The earliest preparation starts with the chlorination of cyclopropylmethylketone with phosphorus pentachloride.[3] Thereafter, the reaction product, 1-cyclopropyl-1,1-dichloroethane, is converted into cyclopropylacetylene via double dehydrochlorination. This occurs in presence of a strongly basic solution, such as potassium tert-butoxide in dimethyl sulfoxide:
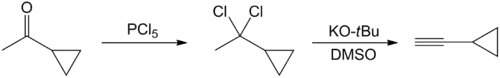
However, the yield of this method is not substantial (20-25%).[4] A one-pot synthesis of cyclopropylacetylene has been reported in which 5-chloro-1-pentyne reacts with n-butyl lithium or n-hexyl lithium. Cyclohexane is used as a solvent. The reaction is a metalation followed by a cyclization. The reaction product is then cooled, and an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is added slowly. There is a two-phase mixture: a heavy water phase and a lighter organic phase containing cyclopropylacetylene.[4]
Applications
Cyclopropylacetylene is used as reagent in organic reactions. It is, for example, a building block of the antiretroviral and psychotropic drug efavirenz. It can also be used in the azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition.
References
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/663018
- "CYCLOPROPYL ACETYLENE". chemicalland21.com. Retrieved 31 May 2017.
- Hudson, C.E.; Bauld, N.L. (1972). "Quantitative analysis of cyclopropyl β hyperfine splittings". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (4): 1158. doi:10.1021/ja00759a021.
- Corley, Edward G.; Thompson, Andrew S.; Huntington, Martha. "CYCLOPROPYLACETYLENE". orgsyn.org. p. 231. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.077.0231. Retrieved 31 May 2017.