Cyclopropanone
Cyclopropanone is an organic compound with molecular formula (CH2)2CO consisting of a cyclopropane carbon framework with a ketone functional group. The parent compound is labile, being highly sensitive toward even weak nucleophiles. Surrogates of cyclopropanone include the acetals.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
cyclopropanone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O | |
| Molar mass | 56.06326 |
| Density | 0.867 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Melting point | −90 °C (−130 °F; 183 K) |
| Boiling point | 50 to 53 °C (122 to 127 °F; 323 to 326 K) at 22 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Cyclopropanone has been prepared by reaction of ketene with diazomethane at −145 °C.[3][4] Derivatives of cyclopropanone are of some interest to organic chemistry.[5]
Derivatives
Cyclopropanones are intermediates in the Favorskii rearrangement with cyclic ketones where carboxylic acid formation is accompanied by ring-contraction.
Cyclopropanones react as 1,3-dipoles in cycloadditions for instance with cyclic dienes such as furan.[6][7] An oxyallyl intermediate or valence tautomer (formed by cleavage of the C2-C3 bond) is suggested as the active intermediate or even a biradical structure (compare to the related trimethylenemethane).
Experimental evidence is not conclusive. Other reactions of cyclopropanones take place through this intermediate. For instance enantiopure (+)-trans-2,3-di-tert-butylcyclopropanone racemizes when heated to 80 °C.[8]
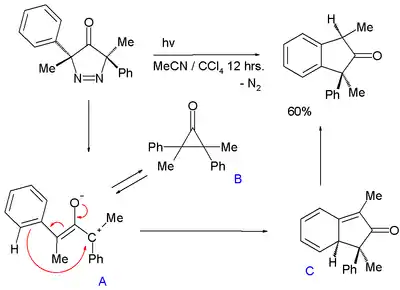
An oxyallyl intermediate is also proposed in the photochemical conversion of a 3,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazole-4-one with expulsion of nitrogen to an indane:[9]
In this reaction oxyallyl intermediate A, in chemical equilibrium with cyclopropanone B attacks the phenyl ring through its carbocation forming a transient 1,3-cyclohexadiene C (with UV trace similar to isotoluene) followed by rearomatization. The energy difference between A and B is 5 to 7 kcal/mol (21 to 29 kJ/mol).
See also
- Other cyclic ketones: cyclobutanone, cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone
- Other cyclopropane derivatives: cyclopropene, cyclopropenone
References
- Salaün, J.; Margueritedoi=10.15227/orgsyn.063.0147, J. (1985). "Cyclopropanone Ethyl Hemiacetal from Ethyl 3-Chloropropanoate". Organic Syntheses. 63: 147. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0147.
- Datasheet commercial supplier Link
- Turro, N.J.; Hammond, W.B. (1968). "Cyclopropanones—VIII". Tetrahedron. 24 (18): 6017–6028. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)90985-8.
- Rothgery, E. F.; Holt, R. J.; McGee, H. A. (1975). "Cryochemical synthesis and molecular energetics of cyclopropanone and some related compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 97 (17): 4971–4973. doi:10.1021/ja00850a034.
- Turro, Nicholas J. (1969). "Cyclopropanones". Accounts of Chemical Research. 2: 25–32. doi:10.1021/ar50013a004.
- Turro, Nicholas J.; Edelson, Simon S.; Williams, John R.; Darling, Thomas R.; Hammond, Willis B. (1969). "Cyclopropanones. XII. Cycloaddition reactions of cyclopropanones". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 91 (9): 2283–2292. doi:10.1021/ja01037a018.
- Edelson, Simon S.; Turro, Nicholas J. (1970). "Cyclopropanones. XVII. Kinetics of the cycloaddition reaction of cyclopropanones with 1,3-dienes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 92 (9): 2770–2773. doi:10.1021/ja00712a030.
- Greene, Frederick D.; Sclove, David B.; Pazos, Jose F.; Camp, Ronald L. (1970). "Thermal reactions of a cyclopropanone. Racemization and decarbonylation of trans-2,3-di-tert-butylcyclopropanone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 92 (25): 7488. doi:10.1021/ja00728a051.
- Moiseev, Andrey G.; Abe, Manabu; Danilov, Evgeny O.; Neckers, Douglas C. (2007). "First Direct Detection of 2,3-Dimethyl-2,3-diphenylcyclopropanone". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (8): 2777–2784. doi:10.1021/jo062259r. PMID 17362038.