Crotonaldehyde
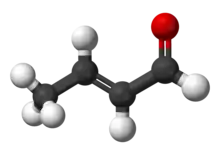
Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.[4]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2E)-but-2-enal | |
| Other names
Crotonaldehyde Crotoinic aldehyde β-Methacrolein β-Methyl acrolein 2-butenal Propylene aldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.846 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 1143 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O | |
| Molar mass | 70.091 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Odor | pungent, suffocating odor |
| Density | 0.846 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −76.5 °C (−105.7 °F; 196.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 104.0 °C (219.2 °F; 377.1 K) |
| 18% (20°C)[2] | |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone soluble in chloroform miscible in benzene |
| Vapor pressure | 19 mmHg (20°C)[2] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4362 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |       |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H301, H310, H311, H315, H318, H330, H335, H341, H373, H400 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P284, P301+310, P302+350, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 13 °C (55 °F; 286 K) |
| 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.1-15.5% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration) |
600 ppm (rat, 30 min) 1375 ppm (rat, 30 min) 519 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 1500 ppm (rat, 30 min)[3] |
LCLo (lowest published) |
400 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 2 ppm (6 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 2 ppm (6 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
50 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkenals |
Acrolein |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and reactivity
Crotonaldehyde is produced by the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde:
- 2 CH3CHO → CH3CH=CHCHO + H2O
Crotonaldehyde is a multifunctional molecule that exhibits diverse reactivity. It is a prochiral dienophile.[5] It is a Michael acceptor. Addition of methylmagnesium chloride produces 3-penten-2-ol.[6]
Polyurethane catalyst N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-1,4-butanediamine (also known as NIAX TMBDA) was obtained by hydrogenating the reaction product of crotonaldehyde and dimethylamine.[7]
Uses
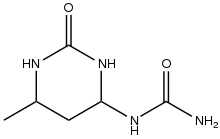
It is a precursor to fine chemicals. Sorbic acid, a food preservative, and trimethylhydroquinone, a precursor to the vitamin E, are prepared from crotonaldehyde. Other derivatives include crotonic acid and 3-methoxybutanol. It adds two equivalents of urea to give the pyrimidine derivative that is employed as a controlled-release fertilizer. [4]
Safety
Crotonaldehyde is a potent irritant even at the ppm levels. It is not very toxic, with an LD50 of 174 mg/kg (rats, oral).[4]
See also
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2599
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0157". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Crotonaldehyde". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- R. P. Schulz, J. Blumenstein, C. Kohlpaintner (2005). "Crotonaldehyde and Crotonic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_083.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Longley Jr., R. I..; Emerson, W. S.; Blardinelli, A. J. (1954). "3,4-Dihydro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-2H-pyran". Org. Synth. 34: 29. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0029.
- Coburn, E. R. (1947). "3-Penten-2-ol". Org. Synth. 27: 65. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.027.0065.
- https://jadedman.wordpress.com/2011/01/08/catalysts/
- Dittmar, Heinrich; Drach, Manfred; Vosskamp, Ralf; Trenkel, Martin E.; Gutser, Reinhold; Steffens, Günter (2009). "Fertilizers, 2. Types". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.n10_n01.
