Cohesin domain
In molecular biology, the cohesin domain is a protein domain. It interacts with a complementary domain, termed the dockerin domain. The cohesin-dockerin interaction is the crucial interaction for complex formation in the cellulosome.[1]
| Cohesin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
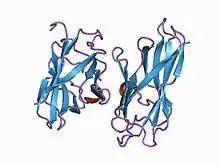 single cohesin domain from the scaffolding protein cipa of the clostridium thermocellum cellulosome | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Cohesin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00963 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0203 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002102 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1anu / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CDD | cd08546 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The scaffoldin component of the cellulolytic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum is a non-hydrolytic protein which organises the hydrolytic enzymes into a large complex, called the cellulosome. Scaffoldin comprises a series of functional domains, amongst which is a single cellulose-binding domain and nine cohesin domains which are responsible for integrating the individual enzymatic subunits into the complex.
References
- Shimon LJ, Bayer EA, Morag E, Lamed R, Yaron S, Shoham Y, Frolow F (March 1997). "A cohesin domain from Clostridium thermocellum: the crystal structure provides new insights into cellulosome assembly". Structure. 5 (3): 381–90. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00195-0. PMID 9083107.
External links
 Media related to Cohesin domain at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cohesin domain at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.