Claude Desgots
Claude Desgots (or Desgotz; c. 1658 – 1732) was a French architect and landscape architect, who designed French formal gardens in France and England.[1] He worked with and was strongly influenced by André Le Nôtre, the designer of the gardens at Vaux-le-Vicomte and Versailles that set the pattern for grand gardening in France up to the Revolution. In spite of increasing competition from the informal English landscape style, the French tradition was kept vital through apprenticeship connections in the generation following Le Nôtre's death in 1700, and a principal representative in this tradition was Claude Desgots, "a worthy heir and a great talent in gardening", remarked the master teacher of architecture Jacques-François Blondel.[2]

Early life and career
Claude Desgots was born in Paris, the son of Pierre II Desgots (1630–1688) and Martine Servelle, who were married in 1654. Pierre II was a landscape designer and draughtsman, who worked closely with André Le Nôtre on the gardens at the Château de Chantilly. He was the son of Le Nôtre's sister, Elisabeth (who was born in 1616 and died sometime before 1640) and Pierre I Desgots (c. 1600 – 1675), who had succeeded his brother Jean Desgots as the gardener of the Tuileries in 1624.[3] In 1675 Claude Desgots was sent on a bursary to the French Academy in Rome, and from c. 1679 he collaborated with his father and Le Nôtre on the gardens at Chantilly.[4] He also worked for a while on the gardens at Versailles and succeeded his father as the gardener of the Tuileries upon the latter's death in 1688.[5]
Later career
When William Bentinck, 1st Earl of Portland was ambassador to Paris in 1698, he convinced Desgots to return with him to England, where Desgots worked out plans for the Queen's House, Greenwich, and parterres for Windsor Castle, in part bringing up to date earlier plans made by Le Nôtre.[6] Nothing came of the English adventure, except that William III of England, who was also Stadthouder in the Netherlands, commissioned him to draw up plans for the gardens at Het Loo, which have recently been replanted to Desgots' designs.
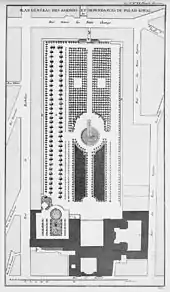
Back in France once more, he was appointed Designer of the parterres of the Royal Houses[7] and Controller of the King's Works,[8] doubtless due to the family connection. He was employed by Phillipe II, duc d'Orléans, the Regent during Louis XV's minority, for whom his design at the Palais Royal introduced smooth hillocks with clipped designs of palmettes, which became a familiar feature of formal French pattern-gardens in the eighteenth century.
Desgots took on as a pupil, c. 1720-25, the Swedish architect and garden designer Carl Hårleman, the close collaborator and correspondent of Carl Gustav Tessin.[9] Hårleman was the prime mover in perpetuating the French formal garden in eighteenth-century Sweden.
In 1730 Desgots published a short biography of André Le Nôtre, which is an important source of information about his mentor.[10]
Personal life
Desgots married Brigide Marion, daughter of Antoine Marion, an employee of the Menus-Plaisirs du Roi and intendant (bursar) of the Marquis of Béringhen, who was Premier Écuyer (First Squire) of the Petite Écurie (Lesser Stables).[5] Their son François Desgots, who became captain of a royal vessel, was one of Le Nôtre's principal heirs.[11] Claude Desgots' son-in-law was Jean-Charles Garnier d'Isle, who succeeded Desgots in 1732 as designer of royal gardens under Louis XV.[5]
Major projects
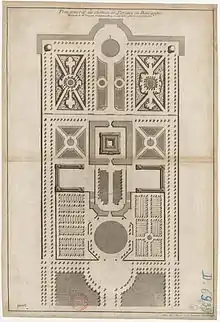
The following projects were identified by Runar Strandberg, 1974:
In France
- Palais du Luxembourg, Paris. Replanning Jacques Boyceau's gardens after the death of the Grande Mademoiselle (1693)[12]
- Clagny. Minor adjustments in Le Nôtre's executed design.
- Rambouillet (for M. Fleuriau d'Armenonville), c. 1705
- Château de Sablé (for Jean-Baptiste Colbert, marquis de Torcy), 1711. Designed the house and gardens.
- Château de Champs, built 1703-07 to designs by J.-B. de Chamblain.
- Château de Meudon, officially from 1715
- Château de Chaville, officially from 1715
- Château d'Anet. Monumental staircase for the duc de Venôme, and new gardens replacing the sixteenth-century parterres of Androuet du Cerceau.
- Château de Perrigny, Burgundy.
- Château de Bagnolet (duchesse d'Orléans), 1727.
- Palais Royal, Paris (for the Regent, Philippe duc d'Orléans, and for his widow), c. 1723-1730.
Abroad
- Schleissheim, Bavaria (for Maximilian Emmanuel, Elector of Bavaria)
- Queen's House, Greenwich, England. 1698. Not executed.
- Windsor Castle, England. 1698. Not executed.
- Het Loo, Netherlands.
References
Notes
- Garrigues 2001, p. 308; Thompson 2006, pp. xi, 30.
- "digne héritier et une grande capacité dans le Jardinage", in Cours d'architecture iv, 3, quoted Strandberg 1974 p49.
- Garrigues 2001, pp. 308 and 315, provides the genealogical details. Elisabeth Le Nôtre married Pierre I Desgots on 2 February 1633. Hazlehurst 1980, pp. 303–323, describes work by Le Nôtre and Pierre II at Chantilly. Taylor 1998 gives the date 1624 for when Pierre Desgots succeeded his brother Jean at the Tuileries.
- Taylor 1998.
- Garrigues 2001, p. 315.
- Strandberg 1974, p 63.
- Dessinateur des parterres des Maisons Royales.
- Controlleur des bâtiments du Roi.
- Their joint archives and drawings form the Hårleman-Tessin Collection, Riksarkivet, Stockholm.
- Desgots 1730.
- Strandberg 1974.
- A signed project is in the Hårleman-Tessin collection, Stockholm
Bibliography
- Desgots, Claude (1730). "Abrégé de la vie d'André Le Nostre", in Continuation des mémoires de littérature et d'histoire, Tome IX, Partie II. Paris: Simart, pp. 459–471 (at Google Books).
- Garrigues, Dominique (2001). Jardins et jardiniers de Versailles au grand siècle. Seyssel: Champ Vallon. ISBN 9782876733374.
- Guiffrey, Jules (1986). André Le Nostre, English translation by George Booth of the 1913 French edition. Lewes, Sussex: The Book Guild. ISBN 9780863321511.
- Hazlehurst, F. Hamilton (1980). Gardens of Illusion: The Genius of André Le Nostre. Nashville, Tennessee: Vanderbilt University Press. ISBN 9780826512093.
- Mariage, Thierry (1999). The World of André Le Nôtre, translated by Graham Larkin. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0812234685.
- Strandberg, Runar (1974). "The French formal garden after Le Nostre", in The French Formal Garden, Elizabeth B. MacDougall and F. Hamilton Hazlehurst, editors. Dumbarton Oaks. Listings at WorldCat.
- Taylor, Susan B. (1998). "Desgots" in The Dictionary of Art, 34 volumes, edited by Jane Turner, reprint with minor corrections. New York: Grove. ISBN 9781884446009.
- Thompson, Ian (2006). The Sun King's Garden. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 9781582346311.