Citromycin
Citromycin is a chemical compound produced by Penicillium.[1] It was first discovered in 1969 and was found to have weak antibiotic activity.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
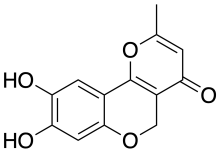
| IUPAC name
8,9-Dihydroxy-2-methyl-5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromen-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 246.218 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Capon, RJ; Stewart, M; Ratnayake, R; Lacey, E; Gill, JH (2007). "Citromycetins and bilains A-C: New aromatic polyketides and diketopiperazines from Australian marine-derived and terrestrial Penicillium spp". Journal of Natural Products. 70 (11): 1746–52. doi:10.1021/np0702483. PMID 17958395.
- Kusakabe, Y; Yamauchi, Y; Nagatsu, C; Abe, H; Akasaki, K (1969). "Citromycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization". The Journal of Antibiotics. 22 (3): 112–8. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.22.112. PMID 4978096.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.