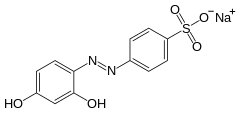
Chrysoine resorcinol
Chrysoine resorcinol is a synthetic azo dye which was formerly used as a food additive. In Europe, it was banned as a food additive in 1977.[1] In the US, it was banned in 1988.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium 4-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)diazenyl]benzenesulfonate | |
| Other names
Sodium p-(2,4-dihydroxyphenylazo)benzenesulfonate; Chrysoine; Resorcinol Yellow; Gold Yellow; Yellow T; Tropaeolin O; Tropaeolin R; C.I. Food Yellow 8; C.I. Acid Orange 6; C.I. 14270 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.114 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H9N2NaO5S | |
| Molar mass | 316.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange-yellow solid |
| Partially soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chrysoine resorcinol can be used as a pH indicator with a color change between pH 11 and pH 12.7. In colorimetry, it has an absorption maximum of 387 nm.
It can be synthesised via the azo coupling of sulfanilic acid and resorcinol.
| Chrysoine resorcinol (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 11.0 | above pH 12.7 | |
| 11.0 | ⇌ | 12.7 |
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
