Chloramben
Chloramben is a selective herbicide used to control the seedlings of broadleaf weeds and annual grasses. It is mostly used for soybeans, but also for dry beans, peanuts, sunflowers, peppers, cotton, sweet potatoes, squash, hardwood trees, shrubs, and some conifers.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
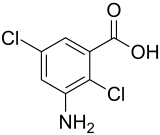
| IUPAC name
3-Amino-2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid | |
| Other names
Ambiben, Amiben | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.658 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5Cl2NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.02 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid[1] |
| Melting point | 194 to 197 °C (381 to 387 °F; 467 to 470 K) (decomposes)[2] 200-201 °C[1] |
| 700 mg/L[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H319, H335, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P271, P280, P281, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
3500 mg/kg (rat)[1] 3725 mg/kg (mouse)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chloramben is considered practically nontoxic.[1]
References
- Chloramben Pesticide Information Profile, Extension Toxicology Network, Oregon State University
- 3-Amino-2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.