Cerberus rynchops
Cerberus rynchops, also known as the New Guinea bockadam, South Asian bockadam, bockadam snake, or dog-faced water snake, is a mildly venomous species of a snake in the family Homalopsidae.[1][2] It is native to coastal waters of South and Southeast Asia.[2] The species was re-delimited in 2012, allocating populations east and south of the west coast of Thailand to other species.[3]
| Cerberus rynchops | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Homalopsidae |
| Genus: | Cerberus |
| Species: | C. rynchops |
| Binomial name | |
| Cerberus rynchops (Schneider, 1799) | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
Ecology and behaviour
It is commonly found in mangroves, mudflats, streams, ponds, tidal pools, on algae patches, and has even been found burrowing into the mud. It is rear-fanged and is mildly venomous. An aquatic and nocturnal snake, it feeds mainly on fish and is known to consume eels.
In captivity, it is observed to move in a sidewinding direction on land. In the BBC series 'Life in Cold Blood' it was filmed adapting this sidewinding technique to jump across a mudflat in Singapore; up until then, no snakes were considered able to truly jump. It also has a prehensile tail that would suggest it could climb mangrove trees. It is now known to give birth to live young, numbering from 8 to 30, either in water or on land.
It is a quite docile, mild-tempered and a hardy snake; in recent years it has become a welcome addition to snake hobbyists in the Philippines. It also owes its popularity to its bright yellow to orange belly coloring, mostly of females. In the Philippines, particularly in the Central Visayas area, this snake is commonly known as the "tangkig".
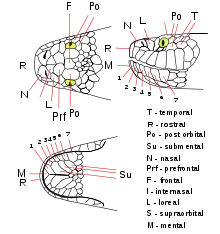
Description
The visibility of upper jaw, giving it a dog-like appearance. Head long and distinct from neck. Eyes small and beady, with rounded pupils. Dorsum dark gray, with faint dark blotches and a dark line along the sides of the head, across the eyes. Center cream with two distinct rows of large, diffuse dark gray spots.
Scales are distinctly keeled. Midbody scale rows 21–25. Ventrals 132–160. Subcaudals 49–72.
Distribution and habitat

This is a saltwater-tolerant species found in India (including Andaman and Nicobar Islands), Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, and northwestern Malaysia.[2] The eastern limit of its distribution with Cerberus schneiderii is uncertain.[3]
References
- Murphy, J. (2010). "Cerberus rynchops". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T176680A7282653. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T176680A7282653.en.
- Cerberus rynchops at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 12 February 2019.
- Murphy, J. C.; Voris, H. K. & Karns, D. R. (2012). "The dog-faced water snakes, a revision of the genus Cerberus Cuvier, (Squamata, Serpentes, Homalopsidae), with the description of a new species". Zootaxa. 3484: 1–34. Abstract (pdf)
- Boulenger, George A. 1890. The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma. Reptilia and Batrachia. Taylor & Francis, London, xviii, 541 pp.
- Karns, D.R.; O'Bannon, A.; Voris,H.K. & Weigt, L.A. 2000. Biogeographical implications of mitochondrial DNA variation in the Bockadam snake (Cerberus rynchops, Serpentes, Homalopsinae) in Southeast Asia. J. Biogeography 27: 391–402
- Schneider, J. G. 1799. Historiae Amphibiorum narturalis et literariae. Fasciculus primus, continens Ranas. Calamitas, Bufones, Salamandras et Hydros. Jena, 266 S.
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080823125843/http://itgmv1.fzk.de/www/itg/uetz/herp/photos/Cerberus_rynchops.jpg
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080823125753/http://itgmv1.fzk.de/www/itg/uetz/herp/photos/Cerberus_rynchops2.jpg
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080823125637/http://itgmv1.fzk.de/www/itg/uetz/herp/photos/Cerberus_rynchops3.jpg
- http://biodiversitycapiz.blogspot.co.za/2013/02/dog-faced-water-snake.html
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070109093424/http://www.wildsingapore.per.sg/discovery/factsheet/snakedogfaced.htm
- http://www.ecologyasia.com/verts/snakes/dog-faced_water-snake.htm
