Capital structure substitution theory
In finance, the capital structure substitution theory (CSS)[1] describes the relationship between earnings, stock price and capital structure of public companies. The CSS theory hypothesizes that managements of public companies manipulate capital structure such that earnings per share (EPS) are maximized. Managements have an incentive to do so because shareholders and analysts value EPS growth. The theory is used to explain trends in capital structure, stock market valuation, dividend policy, the monetary transmission mechanism, and stock volatility, and provides an alternative to the Modigliani–Miller theorem that has limited descriptive validity in real markets. The CSS theory is only applicable in markets where share repurchases are allowed. Investors can use the CSS theory to identify undervalued stocks.[2]
The formula
The CSS theory assumes that company managements can freely change the capital structure of the company – substituting bonds for stock or vice versa – on a day-to-day basis and in small denominations without paying transaction costs. Companies can decide to buy back one single share for the current market price P and finance this by issuing one extra corporate bond with face value P or do the reverse. In mathematical terms these substitutions are defined as
where D is the corporate debt and n the number of shares of company x at time t. The negative sign indicates that a reduction of the number of shares n leads to a larger debt D and vice versa. The earnings-per-share change when one share with price P is repurchased and one bond with face value P is issued:
- The earnings that were ‘allocated’ to the one share that was repurchased are redistributed over the remaining outstanding shares, causing an increase in earnings per share of:
- The earnings are reduced by the additional interest payments on the extra bond. As interest payments are tax-deductible the real reduction in earnings is obtained by multiplying with the tax shield. The additional interest payments thus reduce the EPS by:
Combining these two effects, the marginal change in EPS as function of the total number of outstanding shares becomes:
where
- E is the earnings-per-share
- R is the nominal interest rate on corporate bonds
- T is the corporate tax rate
EPS is maximized when substituting one more share for one bond or vice versa leads to no marginal change in EPS or:
This equilibrium condition is the central result of the CCS theory, linking stock prices to interest rates on corporate bonds.
Capital structure
The two main capital structure theories as taught in corporate finance textbooks are the Pecking order theory and the Trade-off theory. The two theories make some contradicting predictions and for example Fama and French conclude:[3] "In sum, we identify one scar on the tradeoff model (the negative relation between leverage and profitability), one deep wound on the pecking order (the large equity issues of small low-leverage growth firms)...". The capital structure substitution theory has the potential to close these gaps. It predicts a negative relation between leverage and valuation (=reverse of earnings yield) which in turn can be linked to profitability. But it also predicts that high valued small growth firms will avoid the use of debt as especially for these companies the cost of borrowing () is higher than for large companies, which in turn has a negative effect on their EPS. This is consistent with the finding that "…firms with higher current stock prices (relative to their past stock prices, book values or earnings) are more likely to issue equity rather than debt and repurchase debt rather than equity".[4]
Asset pricing
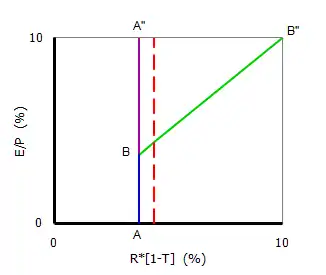
The equilibrium condition can be easily rearranged to an asset pricing formula:

The CSS theory suggests that company share prices are not set by shareholders but by bondholders. As a result of active repurchasing or issuing of shares by company managements, equilibrium pricing is no longer a result of balancing shareholder demand and supply. In a way the CSS theory turns asset pricing upside-down, with bondholders setting share prices and shareholders determining company leverage. The asset pricing formula only applies to debt-holding companies. Some companies are offering stock screeners based on the CSS theory.
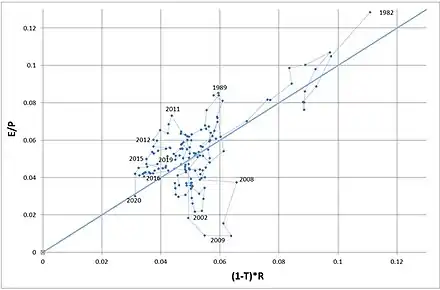
The asset pricing formula can be used on a market aggregate level as well. For the S&P 500 composite index, data from Shiller[5] can be used for composite earnings level, and Federal Reserve Economic Data [6] can be used for the interest rate on corporate bonds (BAA) and an estimate of corporate tax rate (by looking at the ratio of corporate profits and corporate profits after tax).
The resulting graph shows at what times the S&P 500 Composite was overpriced and at what times it was under-priced relative to the Capital Structure Substitution theory equilibrium. In times when the market is under-priced, corporate buyback programs will allow companies to drive up earnings-per-share, and generate extra demand in the stock market. In times when the index was under-priced relative to the model equilibrium, repurchase programs will be stopped and demand is reduced. Not surprisingly the index was overpriced in the period around the tech bubble. What may come more as a surprise that the market is currently (June 2018) not over-priced relative to the model as earnings are high and corporate interest rates are low. In order to reach equilibrium conditions the index would have to gain ~20% or about US$4.9 trillion in market capitalization.
Fed model equilibrium
In the US, a positive relationship between the forward earnings yield of the S&P 500 index and government bond yields has been present over specific time periods, namely 1921 to 1929, and 1987 to 2000; for most other periods, and markets, the relationship fails. This relationship is known as the Fed model, which states an equality between the one year forward looking E/P ratio or earnings yield and the 10-year government bond yield.
The CSS equilibrium condition suggests that the Fed model might be misspecified: the S&P 500 earnings yield during 1987 to 2000 was not in equilibrium with the government bond yield but with the average after-tax interest rate on corporate bonds. The CSS theory suggests that the Fed equilibrium was only observable after 1982, the year in which the United States Securities and Exchange Commission allowed open-market repurchases of shares.[7] However, the CSS theory cannot explain why the Fed model relationship breaks down for all other periods, such as 2000 to 2019.
Dividend policy
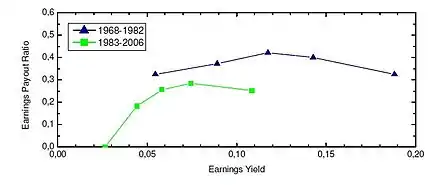
It can be shown that repurchasing has a disadvantage over dividends for companies with a debt-equity ratio above
Under the assumptions described above, low valued, high leveraged companies with limited investment opportunities and a high profitability are expected to use dividends as the preferred means to distribute cash. From the earnings payout graph it can be seen that S&P 500 companies with a low earnings yield (=highly valued) on aggregate changed their dividend policy after 1982, when SEC rule 10b-18 was introduced which allowed public companies open-market repurchases of their own stock.
Monetary policy
An unanticipated 25-basis-point cut in the federal funds rate target is associated with a 1% increase in broad stock indexes in the US.[8] The CSS theory suggests that the monetary policy transmission mechanism is indirect but straightforward: a change in the federal funds rate affects the corporate bond market which in turn affects asset prices through the equilibrium condition.
Corporate tax
One unexpected result of the CSS theory is possibly that a change in corporate tax rate does not have an influence on share prices and/or valuation ratios. As earnings per share are a corporation’s net income after tax, both the numerator and the denominator of the CSS asset pricing formula contain the after-tax factor [1-T] and cancel each other out.
Beta
The CSS equilibrium condition can be used to deduct a relationship for the beta of a company x at time t:
where is the market average interest rate on corporate bonds. The CSS theory predicts that companies with a low valuation and high leverage will have a low beta. This is counter-intuitive as traditional finance theory links leverage to risk, and risk to high beta.
Assumptions
- Managements of public companies manipulate capital structure such that earnings-per-share are maximized.
- Managements can freely change the capital structure of the company – substituting bonds for stock or vice versa – on a day-to-day basis and in small denominations.
- Shares can only be repurchased through open market buybacks. Information about share price is available on a daily basis.
- Companies pay a uniform corporate tax rate T.
See also
References
- Timmer, Jan (2011). "Understanding the Fed Model, Capital Structure, and then Some". SSRN 1322703. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Zürcher, Ulrik Årdal (2014). "The Effect of Interest Rates on Equity Markets That Allows Share Repurchases" (PDF). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Fama, E.F.; French, K.R. (December 2002). "Testing Tradeoff and Pecking Order Predictions About Dividends and Debt". Review of Financial Studies. 15: 1–33. doi:10.1093/rfs/15.1.1. SSRN 199431.
- Hovakimian, A.; Opler, T.; Titman, S. (2001). "The Debt-Equity Choice". Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis. 36 (1): 1–24. doi:10.2307/2676195. JSTOR 2676195.
- Shiller, Robert. "Online Data Robert Shiller". Online Data Robert Shiller.
- "Economic Research". FRED Economic Data. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
- Grullon, G.; Michaely, R. (August 2002). "Dividends, share repurchase, and the substitution hypothesis" (PDF). Journal of Finance. LVII (4): 1649–1684. doi:10.1111/1540-6261.00474.
- Bernanke, B.S.; Kuttner, K.N. (June 2005). "What Explains the Stock Market's Reaction to Federal Reserve Policy?" (PDF). Journal of Finance. LX (3): 1221–1257. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6261.2005.00760.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21.