Camera pedestal
A camera pedestal is an item upon which television cameras are mounted, typically seen in television studios. Unlike tripods, pedestals give camera operators the ability to move the camera in any direction (left, right, forward, back, up, down). They are commonly used on shiny-floor shows, sitcoms and soap operas.
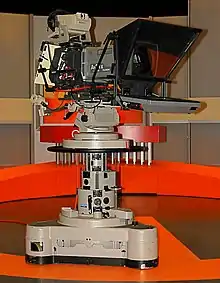
Whilst pedestals are most commonly seen in self-contained television studios, they are also seen on outside broadcasts.[1]
Functionality


A pedestal typically consists of three main parts: a base (with wheels), the column (with steering ring), and the platform. In order to maintain stability and to keep the centre of gravity low, pedestals typically weigh roughly 30% more than their maximum weight capacity meaning that some, such as the Vinten Quattro-L, weigh over 150kg/330lbs.[2]
Base
Manual pedestals have three wheels, allowing them to move along a floor in two ways. This is dictated by Crab/Steer controls on the base.
- Crab mode has all three wheels interlinked to steer in the direction of the steering indicator on the steering ring
- Steer mode locks the position of two wheels but allows the third wheel to turns as the steering ring is rotated
Some pedestals have interchangeable wheels, allowing the studio wheels to be swapped out for OB wheels.[3] On some pedestals, there is a skirt which stops cables from getting caught under the wheels or the base itself. Depending on the model, this can be set manually on each wheel, or across all three wheels.
Column
Pedestals are designed to take the weight of a pan & tilt head, television camera, zoom lens, teleprompter and vanity monitor; this is achieved by having a column balanced with pneumatics or hydraulics. The column, nowadays typically filled with compressed gas such as nitrogen, can be raised and lowered whilst "on-shot".[4] There is a column brake which can be used to keep it at a set position. Locks on the column allow it to be locked down whilst not in use. This means that any change in pressure inside the column (due to temperature change, for example) will not result in damage to camera equipment.
A steering ring, at the top of the column, rotates to control the direction the wheel(s) are pointing. The ring can also be used on some models to adjust the height of the cable skirt.
Pedestals have also been adapted to have removable columns, allowing for it to be mounted directly on dolly tracks or a static base for use in environments where a pedestal would not fit[5]
Robotic pedestals

A number of manufacturers now make robotic camera pedestals, including companies like Shotoku[6] and Vinten Radamec.[7] These are particularly used in news broadcasting environments, where a single camera operator can control multiple cameras in different studios.
The robotic pedestal can be moved around on a studio floor, and the height of the column adjusted, from a remote control panel. Typically, this panel will also control a pan-tilt head fitted on the pedestal, allowing the operator to frame the shot.[8] Some manual pedestals can have a height drive fitted to them allowing for the height of the column to be adjusted remotely - however, someone would still need to reposition the pedestal itself.
References
- "Vinten Quattro Pedestal for Studios and Outside Broadcast". ES Broadcast. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "Vinten Quattro L pedestal Specifications". www.vinten.com. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "Vinten OB Wheel Set for Osprey Elite". www.vinten.com. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- "What is a Studio Pedestal you ask?". YouTube. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "TCS Skquattro peds chosen for 3D broadcast of Swan Lake from St Petersburg". The Guild of Television Camera Professionals. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "SHOTOKU Robotic Pedestal and Height Drives - SmartPed". www.shotoku.tv. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "Vinten FP-188+". www.vinten.com. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- Ringrose, Fergal (3 December 2013). "Heavy payload for new Vinten Rademec ped". SVG Europe. Retrieved 9 January 2019.