CD38-IN-78c
CD38-IN-78c is a drug which acts as a potent and selective inhibitor of the glycoprotein enzyme CD38.[1] In animal studies it boosts levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) in tissues via inhibition of CD38 mediated breakdown of nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), and has been shown to ameliorate metabolic dysfunction associated with the aging process.[2] It also has potential therapeutic application in the treatment of asthma.[3]
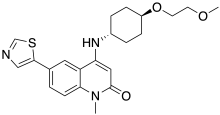 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 413.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Haffner CD, Becherer JD, Boros EE, Cadilla R, Carpenter T, Cowan D, et al. (April 2015). "Discovery, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Thiazoloquin(az)olin(on)es as Potent CD38 Inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 58 (8): 3548–71. doi:10.1021/jm502009h. PMID 25828863.
- Tarragó MG, Chini CC, Kanamori KS, Warner GM, Caride A, de Oliveira GC, Rud M, Samani A, Hein KZ, Huang R, Jurk D, Cho DS, Boslett JJ, Miller JD, Zweier JL, Passos JF, Doles JD, Becherer DJ, Chini EN (May 2018). "A Potent and Specific CD38 Inhibitor Ameliorates Age-Related Metabolic Dysfunction by Reversing Tissue NAD+ Decline". Cell Metabolism. 27 (5): 1081–1095.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.016. PMC 5935140. PMID 29719225.
- Deshpande DA, Guedes AG, Lund FE, Kannan MS (2017). "CD38 in the pathogenesis of allergic airway disease: Potential therapeutic targets". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 172: 116–126. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.12.002. PMC 5346344. PMID 27939939.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.