Butalbital
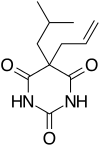
Butalbital is a barbiturate with an intermediate duration of action. Butalbital is often combined with other medications, such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin, for the treatment of pain and headache. The various formulations combined with codeine are FDA-approved for the treatment of tension headaches. Butalbital has the same chemical formula as talbutal but a different structure—one that presents as 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid.[2] Its use for headaches is discouraged (except as a last resort) due to its toxicity and the availability of safer agents.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601009 |
| Routes of administration | oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20-45% |
| Metabolism | hepatic mainly CYP3A4 |
| Elimination half-life | 35 hours [1] |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.926 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 224.260 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Preparations
Combinations include:
- Butalbital and acetaminophen (paracetamol) (trade names: Axocet, Bucet, Bupap, Cephadyn, Dolgic, Phrenilin, Forte, Sedapap)
- Butalbital, paracetamol (acetaminophen), and caffeine (trade names: Fioricet, Esgic, Esgic-Plus, Orbivan)
- Butalbital and aspirin (trade name: Axotal)
- Butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine (trade names: Fiorinal, Fiormor, Fiortal, Fortabs, Laniroif)
- Butalbital, paracetamol (acetaminophen), caffeine, and codeine phosphate (trade name: Fioricet#3 with Codeine)
- Butalbital, aspirin, caffeine, and codeine phosphate (trade name: Fiorinal#3 with Codeine)
- Ergotamine tartrate, caffeine, butalbital, belladonna alkaloids (trade name: Cafergot-PB)
Contraindications
There are specific treatments which are appropriate for targeting migraines and headaches.[4] Butalbital is not recommended as a first-line treatment because it impairs alertness, brings risk of dependence and addiction, and increases the risk that episodic headaches will become chronic.[3] When other treatments are unavailable, butalbital may be appropriate if the patient can be monitored to prevent the development of chronic headache.[3] It is the least preferable option to be used if other available treatments fail.[4]
Side effects
Side effects for any psychoactive drug are difficult to predict, though butalbital is usually well tolerated. Commonly reported side effects for butalbital, some of which tend to subside with continued use, include:
|
Fioricet (50/40/325) |
Rare side-effects include Stevens–Johnson syndrome, an adverse reaction to barbiturates, and anaphylaxis.
The risk and severity of all side effects is greatly increased when butalbital (or butalbital-containing medications) are combined with other sedatives (ex. ethanol, opiates, benzodiazepines, antihistamines). In particular, butalibital, especially when combined with other sedatives (e.g. opioids), can cause life-threatening respiratory depression and death. Inhibitors of the hepatic enzyme CYP3A4 may also increase the risk, severity, and duration of side effects, many drugs inhibit this enzyme as do some foods such as grapefruit and the blood orange. Taking butalbital-based medications with some other drugs may also increase the side effects of the other medication.
Dangers and risks
Butalbital can cause dependence or addiction. Mixing with alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other CNS-depressants increases the risk of intoxication, increases respiratory depression, and increases liver toxicity when in combination with paracetamol (acetaminophen). Use of butalbital and alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other CNS-depressants can contribute to coma, and in extreme cases, fatality.
When benzodiazepines are co-administered with barbiturates, the sum effect of the drugs is far greater than would be expected considering the effect of both drugs separately. This is due to complementary mechanisms at the GABAA receptor, where benzodiazepines increase the rate of chloride channel opening while barbiturates increase the duration. A dose of a benzodiazepine causes a channel which normally opens once every 30 seconds to open 3 times faster, while a barbiturate causes the channel to pass three chloride ions per opening instead of the normal one. When combined, the channel is now passing nine ions every 30 seconds instead of one, a 9-fold increase in activity.
As with most barbiturates, butalbital is a general inducer of P450 enzymes in both rodents and humans, particularly CYP3A4 (hence inducing its own metabolism), CYP2D6, and CYP2C9, although its P450 enzyme induction capability is far less than that of equivalent doses of phenobarbital or secobarbital (the most potent known enzyme inducers in the barbiturate molecular family). At very high doses it has also been demonstrated to induce glutathione S-transferase A1/glutathione S-transferase A2 in rats, although the doses required to achieve this effect to a clinically significant degree fall within the range of butalbital's LD50, making its use for this purpose impractical and highly dangerous (this effect has not yet been tested in human models, it is therefore unknown whether or not GS-T induction plays a significant role in butalbital's effects in humans, or even occurs at all).
References
- "Butalbital and Acetaminophen - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2018-01-21.
- DE Patent 526854
- American Headache Society (September 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Headache Society, archived from the original on 3 December 2013, retrieved 10 December 2013, which cites
- Bigal ME, Lipton RB (April 2009). "Excessive opioid use and the development of chronic migraine". Pain. 142 (3): 179–82. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.01.013. PMID 19232469. S2CID 27949021.
- Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, Scher A, Stewart WF, Lipton RB (September 2008). "Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study". Headache. 48 (8): 1157–68. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01217.x. PMID 18808500. S2CID 17358333.
- Scher AI, Stewart WF, Ricci JA, Lipton RB (November 2003). "Factors associated with the onset and remission of chronic daily headache in a population-based study". Pain. 106 (1–2): 81–9. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00293-8. PMID 14581114. S2CID 29000302.
- Katsarava Z, Schneeweiss S, Kurth T, Kroener U, Fritsche G, Eikermann A, et al. (March 2004). "Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine". Neurology. 62 (5): 788–90. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000113747.18760.D2. PMID 15007133. S2CID 20759425.
- American Academy of Neurology (February 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Neurology, archived from the original on September 1, 2013, retrieved August 1, 2013, which cites
- Silberstein SD (September 2000). "Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- Evers S, Afra J, Frese A, Goadsby PJ, Linde M, May A, Sándor PS (September 2009). "EFNS guideline on the drug treatment of migraine--revised report of an EFNS task force". European Journal of Neurology. 16 (9): 968–81. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02748.x. PMID 19708964. S2CID 9204782.
- Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (2011), Headache, Diagnosis and Treatment of, Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement, archived from the original on 2013-10-29, retrieved 2013-10-24
External links
- Butalbital, Online Medical Dictionary
- Butalbital and Acetaminophen (Systemic) (archive), MedicinePlus Drug Information
- Controlled Substances in Schedule III, (archive), U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration