Bulgarian lands across the Danube
In the Middle Ages the Bulgarian Empire controlled vast areas to the north of the river Danube (with interruptions) from its establishment in 681 to its fragmentation in 1371-1422. These lands were called by contemporary Byzantine historians Bulgaria across the Danube, or Transdanubian Bulgaria (Bulgarian: Отвъддунавска България).[1] Original information for the centuries-old Bulgarian rule there is scarce as the archives of the Bulgarian rulers were destroyed and little is mentioned for this area in Byzantine or Hungarian manuscripts.
First Bulgarian Empire

.png.webp)

After the defeat of Great Bulgaria by the Khazars and following Khan Kubrat's death in 668 a large group of Bulgars followed the third son of the great Khan, Asparukh, who headed south-westwards. In the 670's they were settled in the border area known as the Ongal to the north of the Danube delta. From there Asparukh's cavalry in alliance with local Slavs annually attacked the Byzantine territories in the south. In 680 the Byzantine Emperor Constantine IV lead a large army to face the Bulgars but was defeated in the battle of Ongal and as a result the Byzantines were forced to acknowledge the formation of the First Bulgarian Empire, a direct continuation of Old Great Bulgaria. The northern border of the country followed the southern slopes of the Carpathian mountains from the Iron Gates and reached the Dneper river (or possibly just the Dniester river) to the east.
The Bulgarian's main rivals in the area were the Avars to the west and the Khazars to the east. The latter were a serious threat: after they crushed the resistance of Kubrat's eldest son, Bayan they marched westwards. They waged a war against Asparukh who perished in battle fighting the invaders in 700.
To protect their northern borders, the Bulgarians built several enormous ditches which ran throughout the whole length of the border from the Timok river to the Black Sea.
In 803 Krum became Khan. The new energetic ruler pointed his attention to the north-west where Bulgaria's old enemies, the Avars experienced difficulties and setbacks against the Franks under Charlemagne. Between 804 and 806 the Bulgarian armies militarily annihilated the Avars and destroyed their state. Krum took the eastern parts of the former Avar Khaganate and took over rule of the local Slavic tribes. Bulgaria's territory extended twice from the middle Danube to the north of Budapest to the Dnester though possession of Transylvania is debatable.
In 813 Khan Krum seized Odrin and plundered the whole of Eastern Thrace. He took 50,000 captivities who were settled in Bulgaria across the Danube.
During the First Bulgarian Empire, the Balkan–Danubian culture developed in the 8th century and flourished until the 11th century.[2][3] It represents an early medieval archaeological culture which emerged in the region of the Lower Danube. In Romania it is called Dridu culture[2][3] while in Bulgaria it is usually referred to as Pliska-Preslav culture.[4]
Second Bulgarian Empire
.png.webp)
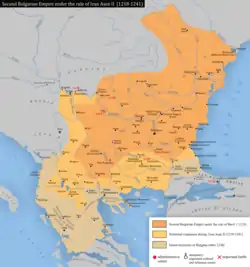

There is evidence that the Second Bulgarian Empire ruled at least nominally the Wallachian lands up to the Rucăr–Bran corridor as late as the late 14th century. In a charter by Radu I, the Wallachian voivode requests that tsar Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria order his customs officers at Rucăr and the Dâmboviţa River bridge to collect tax following the law. The presence of Bulgarian customs officers at the Carpathians indicates a Bulgarian suzerainty over those lands, though Radu's imperative tone hints at a strong and increasing Wallachian autonomy.[5]
Modern geographical equivalents
These are mainly the territories of present-day Romania and as well possibly Hungary, Moldova, Ukraine and Serbia. During the second Bulgarian Empire, until the gradual formation of independent Wallachian and Moldavian principalities, their countries were part of the political geography of Bulgaria, and these countries were administratively and economically organized as Bulgarian regions. However, even after the beginning of the rule of the first Vlach rulers of Basarab, these territories remained under Bulgarian influence.[6]
Language
The Middle Bulgarian language was official and used in Wallachia and Moldova until the end of the 17th century - from the Battle of Hopleja (1655) to the beginning of the rule of the Phanariots (1711-1715). The beginning of the so-called re-romanization was marked by the release of the Bucharest Bible and the Treaty of Karlowitz.
See also
References
- Трансилванските (седмиградските) българи. Етнос. Език. Етнонимия. Ономастика. Просопографии — Сто години след Любомир Милетич в Седмиградско
- Opreanu 2005, p. 127.
- Spinei 2009, p. 87.
- Плиска-Преслав: Прабългарската култура, Том 2, Българска академия на науките Археологически институт и музей, 1981.
- Павлов, Пламен. "За северната граница на Второто българско царство през XIII-XIV в." (in Bulgarian). LiterNet. Retrieved 2009-10-08.
- РОЛЯТА И АДМИНИСТРАТИВНАТА ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ НА Т.НАР. „ОТВЪДДУНАВСКА БЪЛГАРИЯ”
Further reading
- Petăr Koledarov, Političeska geografija na srednovekovnata bălgarska dăržava, vol. 1, Sofija 1979.
- Vasilka Tăpkova-Zaimova, "Roljata i administrativnata organizacija na t. nar. 'otvăd-dunavska Bălgarija'" in Studia Balcanica: proučvanija po slučaj vtorija meždunaroden kongres po balkanistika, Sofija 1970.
- Ian Mladjov, "Trans‐Danubian Bulgaria: Reality and Fiction", in Byzantine Studies/Etudes Byzantines, n.s. 3, 1998 [2000], 85–128.

