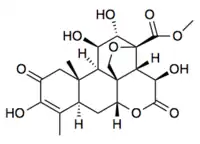
Bruceolide
Bruceolide is a quassinoid that has been isolated from Bischofia javanica. Synthetic derivatives have shown in vitro antimalarial activity.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H26O10 | |
| Molar mass | 438.429 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Murakami, Nobutoshi; Umezome, Takashi; Mahmud, Taifo; Sugimoto, Masanori; Kobayashi, Motomasa; Wataya, Yusuke; Kim, Hye-Sook (March 1998). "Anti-malarial activities of acylated bruceolide derivatives". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 8 (5): 459–462. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(98)00045-6.
- Organization, World Health (1999). WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants. Geneva: World Health Organization. p. 63. ISBN 9241545178.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.