Benzoyl-CoA
Benzoyl-CoA is a molecule implied in the activity of the different enzymes 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA 3-monooxygenase, benzoate-CoA ligase, 2alpha-hydroxytaxane 2-O-benzoyltransferase, anthranilate N-benzoyltransferase, biphenyl synthase, glycine N-benzoyltransferase, ornithine N-benzoyltransferase and phenylglyoxylate dehydrogenase (acylating).
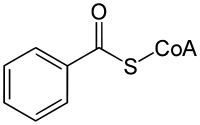 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
benzoyl-S-CoA S-Benzoate coenzyme A | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H36N7O17P3S−4 | |
| Molar mass | 867.60 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is a substrate in the formation of xanthonoids in Hypericum androsaemum by benzophenone synthase, condensing a molecule of benzoyl-CoA with three malonyl-CoA, yielding to 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzophenone. This intermediate is subsequently converted by a benzophenone 3′-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, leading to the formation of 2,3′,4,6-tetrahydroxybenzophenone.[1]
Benzoyl-CoA is a substrate of benzoyl-CoA reductase. This enzyme is responsible in part for the reductive dearomatization of aryl compounds mediated by bacteria under anaerobic conditions.[2]
References
- Alternative pathways of xanthone biosynthesis in cell cultures of Hypericum androsaemum L. Werner Schmidt and Ludger Beerhues, FEBS Letters, Volume 420, Issues 2-3, 29 December 1997, Pages 143-146, doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01507-X
- Matthias Boll , Georg Fuchs , Johann Heider "Anaerobic oxidation of aromatic compounds and hydrocarbons" Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2002 Volume 6, pp. 604–611. doi:10.1016/S1367-5931(02)00375-7