Baptist successionism
Baptist successionism (or Baptist perpetuity) is one of several theories on the origin and continuation of Baptist churches. The theory postulates an unbroken lineage of churches (since the days of John the Baptist, who baptized Christ) which have held beliefs similar to those of current Baptists. Groups often included in this lineage include the Montanists, Paulicians, Cathari, Waldenses, Albigenses, Lollards, and Anabaptists.[1]
Perpetuity
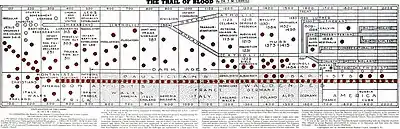
The perpetuity view is often identified with The Trail of Blood, a pamphlet by James Milton Carroll published in 1931.[2] Other Baptist writers who held the perpetuity view are John T. Christian, Thomas Crosby, G. H. Orchard, J. M. Cramp, William Cathcart, Adam Taylor and D. B. Ray.[3]
This view was once commonly held among Baptists.[4] Since the end of the 19th century, however, the theory has increasingly come under attack and today has been largely discredited.[5] Nonetheless, the view continued to be the prevailing view among Baptists of the Southern United States into the latter 20th century.[6] It is now identified primarily with Landmarkism, which is upheld by the Independent Fundamental Baptist movement, though not exclusively so.[7] The concept attempts to parallel the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Anglican doctrine of apostolic succession and stands in contrast to the restorationist views of Latter Day Saints and the Stone-Campbell Restoration Movement.[8]
Contemporary view
Since the end of the 19th century the trend in academic Baptist historiography has been away from the successionist viewpoint to the view that modern day Baptists are an outgrowth of 17th-century English Separatism.[9] This shift precipitated a controversy among Southern Baptists which occasioned the forced resignation of William H. Whitsitt, a professor at Southern Baptist Seminary, in 1898 from the seminary for advocating the new view, though his views continued to be taught in the seminary after his departure.[10]
See also
References
Citations
- Patterson 1969, p. 9.
- McBeth 1987, pp. 59–60.
- McBeth 1987, pp. 59–60; Torbet 1975, p. 18.
- Torbet 1975, p. 18.
- Brackney 2004; McGoldrick 2000.
- Patterson 1969, p. 6.
- McBeth 1987, p. 58; Patterson 1969, p. 6.
- Torbet 1975, p. 19.
- Cross 1990, p. 174.
- McBeth 1987, pp. 457–458.
Works cited
- Brackney, William H. (2004). A Genetic History of Baptist Thought: With Special Reference to Baptists in Britain and North America. Macon, Georgia: Mercer University Press. ISBN 978-0-86554-913-5.
- Cross, I. K. (1990). The Battle For Baptist History. Columbus, Georgia: Brentwood Christian Press. ISBN 978-0-89211-337-8.
- McBeth, H. Leon (1987). The Baptist Heritage: Four Centuries of Baptist Witness. Nashville, Tennessee: Broadman Press. ISBN 978-0-8054-6569-3.
- McGoldrick, James Edward (2000). Baptist Successionism: A Crucial Question in Baptist History. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-3681-5.
- Patterson, W. Morgan (1969). Baptist Successionism: A Critical View. Valley Forge, Pennsylvania: Judson Press. ISBN 978-0-8170-0420-0.
- Torbet, Robert G. (1975). A History of the Baptists (3rd ed.). Valley Forge, Pennsylvania: Judson Press. ISBN 978-0-8170-0074-5.