Aspergillus awamori
Aspergillus awamori is a species of aspergillus that is used to make awamori and shōchū. It can produce citric acid and convert starch to sugar. Aspergillus awamori is often confused with Aspergillus niger as they have very similar morphologies and growth rates at different temperatures, and produce several common.[1] In 1901, Tamaki Inui, lecturer at University of Tokyo succeeded in the first isolating and culturing.[2] In 1910, Genichiro Kawachi succeeded for the first time in cultivating var. kawachi, a variety of subtaxa of A. awamori. This improved the efficiency of shōchū production.[3]
| Aspergillus awamori | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A. awamori grown on citrus pectin agar | |
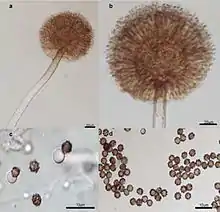 | |
| Electron micrographs of spores | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. awamori |
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus awamori Nakaz. | |
See also
- Aspergillus luchuensis - also known as Aspergillus awamori var. kawachi[4]
References
- 黒麹菌の学名が Aspergillus luchuensis になりました Osamu Yamada
- <8>黒麹菌の役割 発酵中の雑菌繁殖防ぐ Okinawa times
- 初代 河内源一郎(1883~1948) Kawauchi-kin honpo
- "Aspergillus luchuensis". National Center for Biotechnology Information.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.