Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery
Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA or Bland-White-Garland syndrome or White-Garland syndrome) is a rare congenital anomaly in which the left coronary artery (LCA) branches off the pulmonary artery instead of the aortic sinus.[1] After birth, the pressure in other coronary arteries (namely the RCA) will have a pressure that exceeds the LCA and collateral circulation will increase. This, ultimately, can lead to blood flowing from the RCA into the LCA (retrograde) and into the pulmonary artery, thus forming a left-to-right shunt. [2]
| Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bland-White-Garland syndrome |
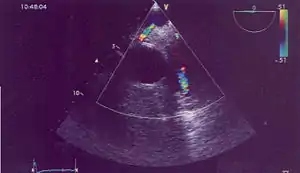 | |
| Possible communication between left coronary artery and pulmonary artery in a 45-year-old woman with Bland-White-Garland syndrome. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
The syndrome is named for Edward Franklin Bland, Paul Dudley White, and Joseph Garland.
References
- "Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery". A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved June 9, 2012.
- Crawford, Michael; DiMarco, John; Paulus, Walter (September 24, 2009). Cardiology (3rd ed.). Mosby. p. 229. ISBN 978-0723434856.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.