Advance Concrete
Advance Concrete is a computer-aided design (CAD) software application was developed by GRAITEC, but is now an Autodesk product,[1] used for modeling and detailing reinforced concrete structures. Advance Concrete is used in the structural / civil engineering and drafting fields.
Features

Advance Concrete is specifically designed for engineers and structural draftsmen looking for comprehensive and easy to use software, including its own graphics engine allowing it to run with or without AutoCAD.
The application can be used for modeling and detailing different types of concrete structures, such as buildings, precast concrete elements, and also for civil engineering designs.
Advance Concrete uses AutoCAD technology: ObjectARX. This technology provides users with professional objects (beams, columns, slabs, bars, frames, stirrup bars) integrated into AutoCAD and on which most basic AutoCAD functions can be applied (stretch, shorten, copy, move). The Advance Concrete native file is the DWG file.
The main functions of Advance Concrete concern:
- 2D / 3D modeling of concrete structures;
- Automated drawings, with tools for automatic creation of sections, elevations, foundations, isometric views, etc.;
- Advanced reinforcement, with automatic creation and update functionalities and also with manual input tools;
- Creation of paper drawings;
- Automatic bill of materials.
- Multi-user modeling. Users can securely and simultaneously work on the same project through a shared database that stores the model data.
The program provides a working environment for creating 3D structural models from which drawings are created. The 3D model is created using Advance Concrete specific objects (structural elements, openings, rebars, etc.) and stored in a drawing (in DWG format). Once a model is complete, Advance Concrete creates all structural and reinforcement drawings using a large selection of tools for view creation, dimensions, interactive annotations, symbols, markings and automatic layout functions. Advance Concrete provides functionalities for automatic drawing updates based on model modifications.
Specific functionalities
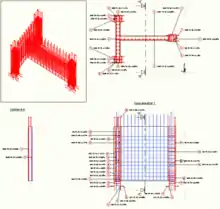
One of the features of Advance Concrete is the “dynamic reinforcement” technology for the rapid reinforcement of concrete elements taking into account their context (type, parameters, connection with other elements). The user creates a so-called dynamic reinforcement solution that integrates the reinforcement cage elements and properties: geometric information, local rules and standards for steel grade, reinforcement bar placement, concrete cover, etc. The reinforcement solutions can be used later for elements that have different sizes. The reinforcement elements adjust to the new dimensions and are taken into account at reinforcement drawing creation and lists. The user can save the reinforcement solution in an external file, which can be exchanged, downloaded, reused in any other projects etc.
Software compatibility
The application is compatible with the following operating systems and Autodesk platforms:
- Windows Vista, Windows XP Pro and Windows 7 (32 and 64 bits)
- AutoCAD 2007, 2008, 2009 32 and 64 bits, 2010 32 and 64 bits
- ADT 2007,
- AutoCAD Architecture 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011.
Software interoperability
Advance Concrete integrates GRAITEC’s “GTC” (GRAITEC Transfer Center) technology, a data synchronization technology that allows:
- Importing / exporting data to other GRAITEC software and standard formats (IFC 2.×3)
- Several Advance Concrete users working simultaneously on the same project and synchronizing their models
- Synchronizing in Advance Concrete the modifications made by engineers in other GRAITEC software applications (e.g., section changes, addition of structural elements, etc.).
GTC is the GRAITEC solution for CAD/Design software interoperability and integration specialized in creating and handling a BIM (Building Information Model).
Release history
| Official name | version | release | date of release |
|---|---|---|---|
| Version 2013 | 2013 | 12 | 2013 |
| Version 2012 | 2012 | 11 | 2012 |
| Version 2011 | 2011 | 10 | 2010 |
| Version 2010 | 2010 | 9 | 2009 |
| Version 2009 | 2009 | 8 | 2009 |
| Version 8.1 | 8.1 | 7 | 2008 |
| Version 7.1 | 7.1 | 6 | 2006 |
| Version 6.1 | 6.1 | 5 | 2005 |
| Version 5.2 | 5.2 | 4 | 2004 |
| Version 5.1 | 5.1 | 3 | 2003 |
| Version 4.2 | 4.2 | 2 | 2002 |
| Version 4.1 | 4.1 | 1 | 2001 |
See also
- Comparison of CAD editors for CAE
- Tekla Structures
References
- "Autodesk Signs Agreement to Acquire Structural Fabrication and Detailing Technology from Graitec". Archived from the original on 2015-12-22.