Adrenochrome
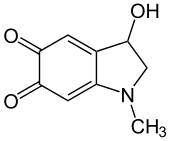
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C9H9NO3 produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). The derivative carbazochrome is a hemostatic medication. Despite a similarity in chemical names, it is unrelated to chrome or chromium.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-5,6-dione | |
| Other names
Adraxone; Pink adrenaline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.176 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 179.175 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 3.264 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 115–120 °C (239–248 °F; 388–393 K) (decomposes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chemistry
In vivo, adrenochrome is synthesized by the oxidation of adrenaline. In vitro, silver oxide (Ag2O) is used as an oxidizing agent.[1] In solution, adrenochrome is pink and further oxidation of the compound causes it to polymerize into brown or black melanin compounds.[2]
Effect on the brain
Several small-scale studies (involving 15 or fewer test subjects) conducted in the 1950s and 1960s reported that adrenochrome triggered psychotic reactions such as thought disorder and derealization.[3] Researchers Abram Hoffer and Humphry Osmond claimed that adrenochrome is a neurotoxic, psychotomimetic substance and may play a role in schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.[4] In what they called the "adrenochrome hypothesis",[5] they speculated that megadoses of vitamin C and niacin could cure schizophrenia by reducing brain adrenochrome.[6][7] The treatment of schizophrenia with such potent anti-oxidants is highly contested. In 1973, the American Psychiatric Association reported methodological flaws in Hoffer's work on niacin as a schizophrenia treatment and referred to follow-up studies that did not confirm any benefits of the treatment.[8] Multiple additional studies in the United States,[9] Canada,[10] and Australia[11] similarly failed to find benefits of megavitamin therapy to treat schizophrenia. The adrenochrome theory of schizophrenia waned, despite some evidence that it may be psychotomimetic, as adrenochrome was not detectable in people with schizophrenia. In the early 2000s, interest was renewed by the discovery that adrenochrome may be produced normally as an intermediate in the formation of neuromelanin. This finding may be significant because adrenochrome is detoxified at least partially by glutathione-S-transferase. Some studies have found genetic defects in the gene for this enzyme.[12]
Legal status
Adrenochrome is unscheduled by the Controlled Substances Act in the United States. It is not an approved drug product by the Food and Drug Administration, and if produced as a dietary supplement it must comply with good manufacturing practice.[13]
In popular culture
- In his 1954 book The Doors of Perception, Aldous Huxley mentioned the discovery and the alleged effects of adrenochrome which he likened to the symptoms of mescaline intoxication, although he had never consumed it.[14]
- Anthony Burgess mentions adrenochrome at the beginning of his 1962 novel A Clockwork Orange. The protagonist and his friends are drinking drug-laced milk: "They had no license for selling liquor, but there was no law yet against prodding some of the new veshches which they used to put into the old moloko, so you could peet it with vellocet or synthemesc or drencrom or one or two other veshches [...]"
- Hunter S. Thompson mentioned adrenochrome in his 1971 book Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas. This is probably the origin of current myths surrounding this compound, because a character states that "There’s only one source for this stuff... the adrenaline glands from a living human body. It’s no good if you get it out of a corpse." The adrenochrome scene also appears in the novel's film adaptation.[14] In the DVD commentary, director Terry Gilliam admits that his and Thompson's portrayal is a fictional exaggeration. Gilliam insists that the drug is entirely fictional and seems unaware of the existence of a substance with the same name. Hunter S. Thompson also mentions adrenochrome in his book Fear and Loathing on the Campaign Trail '72. In the footnotes in chapter April, page 140 he says, "It was sometime after midnight in a ratty hotel room and my memory of the conversation is haze, due to massive ingestion of booze, fatback, and forty cc's of adrenochrome."
- The harvesting of an adrenal gland from a live victim to obtain adrenochrome for drug abuse is a plot feature in the first episode of the television series Lewis (2008).[15]
- The harvest of adrenochrome from murder victims is a key part of the 2017 horror film Adrenochrome. [16]
- Adrenochrome is a component of several false conspiracy theories such as QAnon and the Pizzagate conspiracy theory.[17][18][19]
References
- MacCarthy, Chim, Ind. Paris 55,435(1946)
- A. Hoffer; H. Osmond (22 October 2013). The Hallucinogens. Elsevier. pp. 272–273. ISBN 978-1-4832-6169-0.
- Smythies J (March 2002). "The adrenochrome hypothesis of schizophrenia revisited". Neurotoxicity Research. 4 (2): 147–150. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.3796. doi:10.1080/10298420290015827. PMID 12829415. S2CID 37594882.
- Hoffer A, Osmond H, Smithies J (January 1954). "Schizophrenia; a new approach. II. Result of a year's research". The Journal of Mental Science. 100 (418): 29–45. doi:10.1192/bjp.100.418.29. PMID 13152519.
- Hoffer A (1999). "The Adrenochrome Hypothesis and Psychiatry". The Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine. 14 (1): 49–62.
- Hoffer A, Osmond H (1967). The Hallucinogens. Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-4832-6169-0.
- Hoffer A (1994). "Schizophrenia: An Evolutionary Defense Against Severe Stress" (PDF). Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine. 9 (4): 205–2221.
- Lipton MA, Ban TA, Kane FJ, Levine J, Mosher LR, Wittenborn R (1973). "Task Force Report on Megavitamin and Orthomolecular Therapy in Psychiatry" (PDF). American Psychiatric Association. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Wittenborn JR, Weber ES, Brown M (1973). "Niacin in the Long-Term Treatment of Schizophrenia". Archives of General Psychiatry. 28 (3): 308–315. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1973.01750330010002. PMID 4569673.
- Ban TA, Lehmann HE (1970). "Nicotinic Acid in the Treatment of Schizophrenia: A Summary Report". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 1 (3): 5–7. doi:10.1093/schbul/1.3.5.
- Vaughan K, McConaghy N (1999). "Megavitamin and dietary treatment in schizophrenia: a randomised, controlled trial". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 33 (1): 84–88. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1614.1999.00527.x. PMID 10197889. S2CID 38857700.
- Smythies J (2004). Smythies J (ed.). Disorders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia (1st ed.). Elsevier Academic Press. pp. xv. ISBN 978-0-12-366860-8.
- "Compound summary for adrenochrome". National Center for Biotechnology Information, PubChem Database. Retrieved 2020-01-22.
- Adams J (7 April 2020). "The truth about adrenochrome". The Spinoff. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "Inspector Lewis Series Synopsis". Archived from the original on 2008-06-26.
- "Adrenochrome (2017)".
- "Fear and adrenochrome". Spectator USA. 2020-05-04. Retrieved 2020-05-23.
- "How Facebook connects 'pizzagate' conspiracy theorists". NBC News. Retrieved 2020-05-23.
- Dunning, Brian (October 20, 2020). "Skeptoid #750: How to Extract Adrenochrome from Children". Skeptoid. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
External links
- Adrenochrome Commentary at erowid.org
- Adrenochrome deposits resulting from the use of epinephrine-containing eye drops used to treat glaucoma from the Iowa Eye Atlas (searched for diagnosis = adrenochrome)