AZGP1
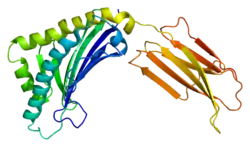
Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AZGP1 gene.[5][6]
This gene expresses a soluble protein that stimulates lipolysis, induces a reduction in body fat in mice, is associated with the cachexia related to cancer, and is known to be expressed in secretory cells of lung epithelium.[7] In 2009, it was found that smoking increases expression of this gene, which is why smoking cessation leads to weight gain.[7] Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein levels also rise with onset of Diabetes 2, which accounts for weight loss thereafter.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000160862 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000037053 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Ueyama H, Niwa M, Tada T, Sasaki M, Ohkubo I (Jul 1991). "Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a human Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein cDNA and chromosomal assignment of its gene". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 177 (2): 696–703. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)91844-3. PMID 2049092.
- "Entrez Gene: AZGP1 alpha-2-glycoprotein 1, zinc-binding".
- Vanni, H; Kazeros, A; Wang, R; Harvey, BG; Ferris, B; De, BP; Carolan, BJ; Hübner, RH; et al. (2009). "Cigarette Smoking Induces Overexpression of a Fat-Depleting Gene AZGP1 in the Human". Chest. 135 (5): 1197–208. doi:10.1378/chest.08-1024. PMC 2679098. PMID 19188554.
External links
- Human AZGP1 genome location and AZGP1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Freije JP, Fueyo A, Uría J, López-Otín C (1991). "Human Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein cDNA cloning and expression analysis in benign and malignant breast tissues". FEBS Lett. 290 (1–2): 247–9. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)81271-9. PMID 1915885. S2CID 2058665.
- Tada T, Ohkubo I, Niwa M, et al. (1991). "Immunohistochemical localization of Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein in normal human tissues". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39 (9): 1221–6. doi:10.1177/39.9.1918940. PMID 1918940.
- Araki T, Gejyo F, Takagaki K, et al. (1988). "Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein and its homology to histocompatibility antigens". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (3): 679–83. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.3.679. PMC 279618. PMID 3422450.
- Shibata S, Miura K (1982). "Nephritogenic glycoprotein. IX. Plasma Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein as a second source of nephritogenic glycoprotein in urine". Nephron. 31 (2): 170–6. doi:10.1159/000182638. PMID 6896906.
- Ueyama H, Deng HX, Ohkubo I (1994). "Molecular cloning and chromosomal assignment of the gene for human Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein". Biochemistry. 32 (48): 12968–76. doi:10.1021/bi00211a004. PMID 8241150.
- Freije JP, Fueyo A, Uría JA, et al. (1994). "Human Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein: complete genomic sequence, identification of a related pseudogene and relationship to class I major histocompatibility complex genes". Genomics. 18 (3): 575–87. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80359-3. PMID 8307568.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Sánchez LM, López-Otín C, Bjorkman PJ (1997). "Biochemical characterization and crystalization of human Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein, a soluble class I major histocompatibility complex homolog". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (9): 4626–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.9.4626. PMC 20774. PMID 9114041.
- Brysk MM, Lei G, Rajaraman S, et al. (1997). "Gene expression of zinc-alpha 2-glycoprotein in normal human epidermal and buccal epithelia". In Vivo. 11 (3): 271–4. PMID 9239523.
- Lei G, Arany I, Selvanayagam P, et al. (1997). "Detection and cloning of epidermal zinc-alpha 2-glycoprotein cDNA and expression in normal human skin and in tumors". J. Cell. Biochem. 67 (2): 216–22. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19971101)67:2<216::AID-JCB6>3.0.CO;2-#. PMID 9328826.
- Ogikubo O, Maeda T, Yamane T, et al. (1998). "Regulation of Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein-mediated cell adhesion by kininogens and their derivatives". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 252 (1): 257–62. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9614. PMID 9813179.
- Sánchez LM, Chirino AJ, Bjorkman P (1999). "Crystal structure of human ZAG, a fat-depleting factor related to MHC molecules". Science. 283 (5409): 1914–9. doi:10.1126/science.283.5409.1914. PMID 10206894.
- Lei G, Brysk H, Arany I, et al. (1999). "Characterization of zinc-alpha(2)-glycoprotein as a cell adhesion molecule that inhibits the proliferation of an oral tumor cell line". J. Cell. Biochem. 75 (1): 160–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19991001)75:1<160::AID-JCB16>3.0.CO;2-B. PMID 10462714.
- Davidsson P, Nilsson CL (2000). "Peptide mapping of proteins in cerebrospinal fluid utilizing a rapid preparative two-dimensional electrophoretic procedure and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1473 (2–3): 391–9. doi:10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00197-x. PMID 10594376.
- Kennedy MW, Heikema AP, Cooper A, et al. (2001). "Hydrophobic ligand binding by Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein, a soluble fat-depleting factor related to major histocompatibility complex proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (37): 35008–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100301200. PMID 11425849.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Scherer SW, Cheung J, MacDonald JR, et al. (2003). "Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and biology". Science. 300 (5620): 767–72. doi:10.1126/science.1083423. PMC 2882961. PMID 12690205.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7". Nature. 424 (6945): 157–64. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- BURGI W, SCHMID K (1998). "Preparation and properties of Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein of normal human plasma". J. Biol. Chem. 236: 1066–74. PMID 13689030.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.