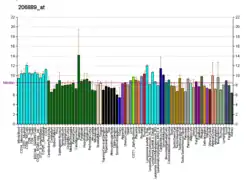
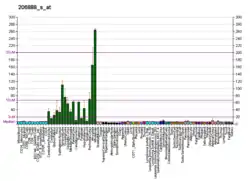
ARHGDIG
Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGDIG gene.[5][6][7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000242173 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000073433 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Adra CN, Manor D, Ko JL, Zhu S, Horiuchi T, Van Aelst L, Cerione RA, Lim B (May 1997). "RhoGDIγ: A GDP-dissociation inhibitor for Rho proteins with preferential expression in brain and pancreas". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 94 (9): 4279–84. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.9.4279. PMC 20713. PMID 9113980.
- Brunet N, Morin A, Olofsson B (Apr 2002). "RhoGDI-3 regulates RhoG and targets this protein to the Golgi complex through its unique N-terminal domain". Traffic. 3 (5): 342–57. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30504.x. PMID 11967128.
- "Entrez Gene: ARHGDIG Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) gamma".
- Zalcman G, Closson V, Camonis J, Honoré N, Rousseau-Merck MF, Tavitian A, Olofsson B (Nov 1996). "RhoGDI-3 is a new GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI). Identification of a non-cytosolic GDI protein interacting with the small GTP-binding proteins RhoB and RhoG". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (48): 30366–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.48.30366. PMID 8939998.
External links
- Human ARHGDIG genome location and ARHGDIG gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Zalcman G, Closson V, Camonis J, Honoré N, Rousseau-Merck MF, Tavitian A, Olofsson B (1997). "RhoGDI-3 is a new GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI). Identification of a non-cytosolic GDI protein interacting with the small GTP-binding proteins RhoB and RhoG". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (48): 30366–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.48.30366. PMID 8939998.
- Adra CN, Iyengar AR, Syed FA, Kanaan IN, Rilo HL, Yu W, Kheraj R, Lin SR, Horiuchi T, Khan S, Weremowicz S, Lim B, Morton CC, Higgs DR (1998). "Human ARHGDIG, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for Rho proteins: genomic structure, sequence, expression analysis, and mapping to chromosome 16p13.3". Genomics. 53 (1): 104–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5482. PMID 9787082.
- Elenich LA, Nandi D, Kent AE, McCluskey TS, Cruz M, Iyer MN, Woodward EC, Conn CW, Ochoa AL, Ginsburg DB, Monaco JJ (1999). "The complete primary structure of mouse 20S proteasomes". Immunogenetics. 49 (10): 835–42. doi:10.1007/s002510050562. PMID 10436176. S2CID 20977116.
- Daniels RJ, Peden JF, Lloyd C, Horsley SW, Clark K, Tufarelli C, Kearney L, Buckle VJ, Doggett NA, Flint J, Higgs DR (2001). "Sequence, structure and pathology of the fully annotated terminal 2 Mb of the short arm of human chromosome 16". Hum. Mol. Genet. 10 (4): 339–52. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.4.339. PMID 11157797.
- Li X, Bu X, Lu B, Avraham H, Flavell RA, Lim B (2002). "The Hematopoiesis-Specific GTP-Binding Protein RhoH Is GTPase Deficient and Modulates Activities of Other Rho GTPases by an Inhibitory Function". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (4): 1158–71. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.4.1158-1171.2002. PMC 134637. PMID 11809807.
- del Pozo MA, Alderson NB, Kiosses WB, Chiang HH, Anderson RG, Schwartz MA (2004). "Integrins regulate Rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains". Science. 303 (5659): 839–42. doi:10.1126/science.1092571. PMID 14764880. S2CID 22871247.
- Dransart E, Morin A, Cherfils J, Olofsson B (2005). "Uncoupling of inhibitory and shuttling functions of rho GDP dissociation inhibitors". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (6): 4674–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409741200. PMID 15513926.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.