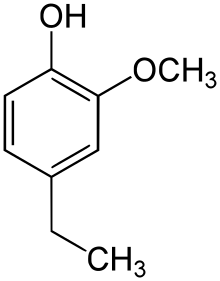
4-Ethylguaiacol
4-Ethylguaiacol, often abbreviated to 4-EG, is a phenolic compound with the molecular formula C9H12O2. It can be produced in wine and beer by Brettanomyces.[2] It is also frequently present in bio-oil produced by pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Ethyl-2-methoxyphenol | |
| Other names
p-Ethylguaiacol Homocresol Guaiacyl ethane 2-Methoxy-4-ethylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.637 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 152.193 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1064 kg/m3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 15 °C (59 °F; 288 K) |
| Boiling point | 235.1 °C (455.2 °F; 508.2 K) [1] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S37/39 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Winemaking
It is produced along with 4-ethylphenol (4-EP) in wine and beer by the spoilage yeast Brettanomyces.[2] When it is produced by the yeast to concentrations greater than the sensory threshold of >600 µg/L, it can contribute bacon, spice, clove, or smoky aromas to the wine. On their own these characters can be quite attractive in a wine, however as the compound usually occurs with 4-EP whose aromas can be more aggressive, the presence of the compound often signifies a wine fault. The ratio in which 4-EP and 4-EG are present can greatly affect the organoleptic properties of the wine.
Bio-oil
4-Ethylguaiacol can also be produced by pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. It is produced from the lignin, along with many of the other phenolic compounds present in bio-oil. In particular, 4-ethylguaiacol is derived from guaiacyl in the lignin.[3]
See also
References
- Mozaffari, Parsa; Järvik, Oliver; Baird, Zachariah Steven (2020-10-28). "Vapor Pressures of Phenolic Compounds Found in Pyrolysis Oil". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. doi:10.1021/acs.jced.0c00675. ISSN 0021-9568.
- Caboni, Pierluigi; Sarais, Giorgia; Cabras, Marco; Angioni, Alberto (2007). "Determination of 4-Ethylphenol and 4-Ethylguaiacol in Wines by LC-MS-MS and HPLC-DAD-Fluorescence". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 55 (18): 7288–93. doi:10.1021/jf071156m. PMID 17676867.
- Lyu, Gaojin; Wu, Shubin; Zhang, Hongdan (2015). "Estimation and Comparison of Bio-Oil Components from Different Pyrolysis Conditions". Frontiers in Energy Research. 3. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2015.00028. ISSN 2296-598X.
