2006 European blackout
The 2006 European blackout was a major blackout which occurred on Saturday, November 4, 2006. More than 15 million clients of the Union for the Co-ordination of Transmission of Electricity (UCTE) did not have access to electricity during about two hours on this date. It resulted in dozens of people trapped in elevators, numerous trains were halted, and the emergency services were receiving an overwhelming number of calls.[1] The immediate action taken by the Transmission System Operators (TSO) prevented the disturbance from turning into a Europe-wide blackout.
Cause
The cause of this major blackout was a planned routine disconnection of the Ems powerline crossing in Northwest Germany to allow a ship to pass beneath the overhead cables. In September, the shipyard had requested the lines, called Conneforde–Diele red and white, to be shut off starting at 01:00 on 5 November. This change was communicated to the neighboring TSOs and they did simulations to ensure stability. As a result, the planned power flow between TSOs was decreased for 00:00 to 06:00 5 November. On 3 November, the shipyard requested the shut-off to be advanced to 22:00 on 4 November. E.ON Netz thought that this would be more favorable and approved the request. However, this change was not communicated to the neighboring TSOs until very late so a full analysis was not done.[2] Also, the transfer capacity had already been sold and it was not possible to change it except for force majeure.
Once the second circuit was turned off, this caused alarms due to high power flow. Also the Landesbergen–Wehrendorf line was very close to its limit. Over the next half-hour, the power first went down but then it crept back up. E.ON Netz thought that closing a bus tie would decrease this a bit; in fact, it had the opposite effect and once this was performed the line tripped out.
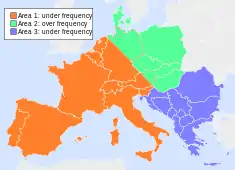
Twenty eight seconds later, an electrical blackout had cascaded across Europe extending from Poland in the north-east, to the Benelux countries and France in the west, through to Portugal, Spain and Morocco in the south-west, and across to Greece and the Balkans in the south-east.
Timeline
- 21:29 - E.ON Netz made load flow calculations and there were no indications of any violation of limit values. Without any calculations, E.ON Netz staff assumed that the N-1 criterion would be met in the system once the Conneforde-Diele line was switched. [3]
- 21:30 - Before the Conneforde-Diele line was opened, RWE TSO’s calculations showed that, even though the RWE TSO grid would be highly loaded, it would still be secure. [3]
- 21:38 - E. ON Netz switched off the first circuit of the 380 kV Conneforde-Diele line.[3]
- 21:39 - E.ON Netz switched off the second circuit of the 380 kV Conneforde-Diele line. E.ON Netz soon received several warning messaged of high power flow in the Elsen-Twistetal and Elsen-Bechterdissen lines.[3]
- 21:41 - RWE TSO informed E. ON Netz that the Landesbergen-Wehrendorf line (an interconnection line between E. ON Netz and RWE TSO) was still under the given limit (1,795 A) and that the N-1 criterion was still met in the internal RWE TSO network. The protection settings on both sides of the line are different.[3]
- 22:00 - Every full hour, the commercial schedule changes were set. Consumption in E. ON Netz was about 13,500 MW and the injected wind power accounted for 3,300 MW. Due to transits, the lines towards the West were already loaded; this situation was normal.[3]
- 22:05 - Suddenly the load flow situation changed unexpectedly and resulted in a fast increase of the load on the Landesbergen-Wehrendorf line by 100 MW.[3]
- 22:06 - The current in the Landesbergen-Wehrendorf line increased to 1900 A within 2-3 minutes. The safety limit value of 1800 A (specified by RWE) was exceeded on the line.[3]
- 22:10:11 - Because of the rush, E.ON Netz made the coupling without any coordination with RWE. The switching measure was meant to reduce the load flow of the Landesbergen-Wehrendorf line.[3]
- 22:10:13 - The Landesbergen-Wehrendorf line was first tripped automatically by the protective device. The 220 kV Bielefeld/Ost-Gütersloh line and the 280 kV Bechterdissen-Elsen line were also tripped.[3]
- 22:10:28 - The UCTE SYSTEM was split shortly after the tripping of the interconnection lines between E. ON Netz and RWE TSO, internal E.ON Netz lines, internal lines in APG (AT), interconnection lines between HEP (HR) and MAVIR (HU), and the internal lines in HEP (HR) and MAVIR (HU).[3]
- 22:10:32 - All interconnection lines between Morocco and Spain tripped due to the low frequency.[3]
Affected areas
In total, over 10 million people in northern Germany, France, Italy, Belgium, and Spain lost power or were affected by the blackout. In northern Germany, more than 100 trains were delayed for more than two hours because of the blackout.[4] Almost all of France was affected except the southeast of the country.[4] In affected areas in France, firefighters were asked to respond to approximately 40 people being stuck in elevators. In Belgium, only the area around Antwerp was seriously affected, as well as Ghent and Liège, leaving the rest of the country with power.[5] Italy, which had experienced a similar blackout in 2003 which left 95% of the country without power, was only affected in a few areas, mainly Piedmont, Liguria in northern Italy, and Puglia in southern Italy.[5] In Spain, the news network Red Electrica was affected, as were the regions of Madrid, Barcelona, Zaragoza, and part of Andalusia.[4]
Aftermath
The UCTE (Union for the Coordination of the Transmission of Electricity) and TSO (Transmission System Operator) acted swiftly, and were able to restore electricity shortly, however the event highlighted glaring problems. The UCTE and TSO were victims of enormous backlash from the media and the citizens, and there were threats that both corporations might undergo serious managerial overhauls. This forced both companies to go back to the drawing board, and determine what possible improvements could be made to prevent such a problem in the future. For starters, the UCTE strengthened its defense system by using blackout simulations with the help of numerical analysis, and sophisticated technology. Using these simulations, they were able to bring to life realistic scenarios that could impact these regions in the future, and how the TSO could possibly combat the problems. This initiated the tweaking of the N-1 criterion in Policy 3 of the UCTE Operation Handbook.[6] Essentially, the interconnected power systems were decentralized, wherein different border lines were responsible for the power lines running through them, rather than one general body governing the entire system. This process was later known as Resynchronization, and it was able to increase stability within the UCTE if any problems were to arise. Furthermore, joint-training workshops[6] were established that would assure that regional dispatchers would have the knowledge and skills to operate the power systems, and would have the ability to implement the solutions given by the TSO under any circumstances.
Possible political influences
Centralised vs decentralised governments
Although it may seem an abstract concept, the political system may have played a role in this power outage happening. At the time, many EU policy makers pushed for a more centralised form of government. This would give the government as a whole a greater role in regulating Europe's power grids. When the Blackout of 2006 occurred, these policy makers said this event revealed the fragility of Europe's current power grid system and called on a formal centralised government.[7] On the flip-side, however, because the power disturbances were quickly contained and dealt with, the power sector spokesperson cited this event as a confirmation of the reliability of the current, transnational power grids and praised the decentralised governance model in place at the time.
Security
It comes as a surprise that, since the 2003 blackout, the security system had gone unchanged. The security system did not account for an increase of liberalization of electric supply which caused an increase in cross-border trades, which are not properly accounted for when reviewing the security of the system. Also, due to the decentralized form of government at the time, the transmission system operator, or TSO, would each control their own area, and exchange little information with other TSOs. This inevitably resulted in a slow response time to contingencies. To repair these fallacies so something like this would not occur in the future, a new mode of coordinated operation for real-time security would be needed. But in order to do so, those implementing this would need to overcome a series of psychological, organizational, and legal challenges. The alternative of this would be to risk yet another major blackout or run the current system very conservatively, which would cause an astronomical cost to the consumers.[8]
See also
References
- "Q&A: Europe's power blackout". BBC. 2006-11-06. Retrieved 2018-06-26.
- Blackout of November 2006: important lessons to be drawn, European Commission press release
- Li, Chunyan; Sun, Yuanzhang; Chen, Xiangyi (December 2007). "Analysis of the blackout in Europe on November 4, 2006". 2007 International Power Engineering Conference (IPEC 2007): 939–944.
- "Brief blackout affects 10 million across Europe - Europe - International Herald Tribune". The New York Times. 2006-11-05. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2018-02-16.
- McMahon, Barbara (2006-11-06). "Millions blacked out across Europe as cold snap triggers power surge". the Guardian. Retrieved 2018-02-16.
- "Final Report: System Disturbance on 4 November 2006" (PDF): 84. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Van Der Vleuten, Erik; Lagendijk, Vincent (2010-04-01). "Interpreting transnational infrastructure vulnerability: European blackout and the historical dynamics of transnational electricity governance". Energy Policy. 38 (4): 2053–2062. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.030. ISSN 0301-4215.
- Bialek, J. W. (July 2007). "Why has it happened again? Comparison between the UCTE blackout in 2006 and the blackouts of 2003". 2007 IEEE Lausanne Power Tech: 51–56. doi:10.1109/PCT.2007.4538291. ISBN 978-1-4244-2189-3.