1990s in Bangladesh
The 1990s (pronounced "nineteen-nineties", commonly shortened as the "'90s", pronounced "nineties") was a decade of the Gregorian calendar that began on January 1, 1990, and ended on December 31, 1999. For Bangladesh this decade was characterized by transition to democracy, rapid urbanisation and globalization and struggle for free and fair elections. The newly earned democracy influenced the cultural activities in the decade.

Politics and National life
Transition to democracy
The decade began with the country agitating against the rule of incumbent President Ershad. A wide umbrella of political parties united against Ershad. Ziaur Rahman's widow, Khaleda Zia, led the Bangladesh Nationalist Party, which allied with the Bangladesh Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman's daughter Sheikh Hasina. Jamaat-e-Islami Bangladesh and other Islamic parties and alliances joined the opposition ranks. They called for strikes and protests that paralysed the state and its economy. Although the parliament was dissolved, fresh elections were boycotted by the opposition, including Awami League and Jamaat. Students launched an intensifying opposition campaign, which ultimately forced Ershad to step down. On 6 December 1990, Ershad offered his resignation.[1] On 27 February 1991, after two months of widespread civil unrest, an interim government headed by Acting President Chief Justice Shahabuddin Ahmed oversaw what most observers believed to be the nation's most free and fair elections to that date.[2]
First Khaleda administration, 1991–96

The centre-right Bangladesh Nationalist Party won a plurality of seats and formed a government with support from the Islamic party Jamaat-I-Islami, with Khaleda Zia, widow of Ziaur Rahman, obtaining the post of prime minister. Only four parties had more than 10 members elected to the 1991 Parliament: The BNP, led by Prime Minister Begum Khaleda Zia; the AL, led by Sheikh Hasina; the Jamaat-I-Islami (JI), led by Ghulam Azam; and the Jatiya Party (JP), led by acting chairman Mizanur Rahman Choudhury while its founder, former President Ershad, served out a prison sentence on corruption charges. The electorate approved still more changes to the constitution, formally re-creating a parliamentary system and returning governing power to the office of the prime minister, as in Bangladesh's original 1972 constitution. In October 1991, members of Parliament elected a new head of state, President Abdur Rahman Biswas.[2]
In March 1994, controversy over a parliamentary by-election, which the opposition claimed the government had rigged, led to an indefinite boycott of Parliament by the entire opposition. The opposition also began a program of repeated general strikes to press its demand that Khaleda Zia's government resign and a caretaker government supervise a general election. Efforts to mediate the dispute, under the auspices of the Commonwealth Secretariat, failed. After another attempt at a negotiated settlement failed narrowly in late December 1994, the opposition resigned en masse from Parliament. The opposition then continued a campaign of marches, demonstrations, and strikes in an effort to force the government to resign. The opposition, including the Bangladesh Awami League, led by Sheikh Hasina, pledged to boycott national elections scheduled for 15 February 1996.[2]
In February, Khaleda Zia was re-elected by a landslide in voting boycotted and denounced as unfair by the three main opposition parties. In March 1996, following escalating political turmoil, the sitting Parliament enacted a constitutional amendment to allow a neutral caretaker government to assume power and conduct new parliamentary elections; former Chief Justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman was named Chief Adviser (a position equivalent to Prime Minister) in the interim government. New parliamentary elections were held in June 1996 and the Awami League won plurality and formed the government with support from the Jatiya Party led by deposed president Hussain Muhammad Ershad; party leader Sheikh Hasina became Prime Minister of Bangladesh.[2]
First Hasina administration, 1996–2001

Sheikh Hasina formed what she called a "Government of National Consensus" in June 1996, which included one minister from the Jatiya Party and another from the Jatiya Samajtantrik Dal. The Jatiya Party never entered into a formal coalition arrangement, and party president Hussain Muhammad Ershad withdrew his support from the government in September 1997. Only three parties had more than 10 members elected to the 1996 Parliament: the Awami League, BNP, and Jatiya Party. Jatiya Party president, Ershad, was released from prison on bail in January 1997.[2]
International and domestic election observers found the June 1996 election free and fair, and ultimately, the Bangladesh Nationalist Party decided to join the new Parliament. The BNP soon charged that police and Bangladesh Awami League activists were engaged in large-scale harassment and jailing of opposition activists. At the end of 1996, the Bangladesh Nationalist Party staged a parliamentary walkout over this and other grievances but returned in January 1997 under a four-point agreement with the ruling party. The Bangladesh Nationalist Party asserted that this agreement was never implemented and later staged another walkout in August 1997. The Bangladesh Nationalist Party returned to Parliament under another agreement in March 1998.[2]
In June 1999, the Bangladesh Nationalist Party and other opposition parties again began to abstain from attending Parliament. Opposition parties staged an increasing number of nationwide general strikes, rising from six days of general strikes in 1997 to 27 days in 1999. A four-party opposition alliance formed at the beginning of 1999 announced that it would boycott parliamentary by-elections and local government elections unless the government took steps demanded by the opposition to ensure electoral fairness. The government did not take these steps, and the opposition subsequently boycotted all elections, including municipal council elections in February 1999, several parliamentary by-elections, and the Chittagong city corporation elections in January 2000.[2]
Administrative Division
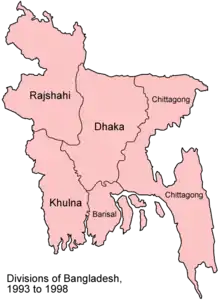
In 1990, Bangladesh was administratively divided into 4 divisions, namely Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna and Rajshahi which were further subdivided into a total of 64 districts (See List of districts of Bangladesh). The government of under Begum Khaleda Zia chose to change the upazila system and set up instead democratically designed decentralised structures at the appropriate levels.[3] In 1993, Barisal Division was split off from Khulna Division and in 1995, Sylhet Division was split off from Chittagong Division. By the end of the decade, the number of divisions stood at 6.
Demographics
Based on World Development Indicators published by the World Bank[4] the population of Bangladesh grew from 104 million at the beginning of the decade to 129 million by the end. This signifies an annual population growth rate of 2.2%. Population density increased from 796 to 991 per sq. km.
The urban population was 19.8% of the total at the beginning, which ended up at 23.2%. Dhaka, the largest city, with a population of 6.6 million, accounted for 31.5% of the total urban population by 1999. United Nations World Population Prospects[4] show that the population growth rate was in decreasing trend (from 2.5% per annum to 2.0%), primarily due to reduction in fertility rate (births per woman) from 4.5 to 3.3. Life expectancy at birth increased from 58.4 years to 64.7 years with Child (0-5) mortality reducing from 144 per 1,000 births to 92. Age dependency ratio (% of working-age population) changed from 83.3% to 70.7% by the end of the decade.
Climate
Temperature and Precipitation
| Climate data for Bangladesh in 1990s | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.3 (64.9) |
20.9 (69.6) |
25.1 (77.2) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.1 (82.6) |
27.9 (82.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.3 (66.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 9.1 (0.36) |
30.6 (1.20) |
58.2 (2.29) |
145.6 (5.73) |
267.2 (10.52) |
419.3 (16.51) |
521.4 (20.53) |
424.1 (16.70) |
332.6 (13.09) |
168.5 (6.63) |
37.6 (1.48) |
8.7 (0.34) |
2,422.9 (95.38) |
| Source: Climatic Research Unit (CRU) of University of East Anglia (UEA)[5] | |||||||||||||
Compared to prior decade the average December temperature decreased by about 0.6 degree but moderate increases in other months offset the overall annual impact. Average rainfall decreased for April, May and July leading to overall average annual rainfall decrease by about 70mm.[5]
Natural disasters

The severe cyclone of 1991 and the devastating floods of 1998 marks this decade as one of the worst hit by natural disasters after independence.
The 1991 Bangladesh cyclone was among the deadliest tropical cyclones on record. On the night of 29 April 1991, it struck the Chittagong district of southeastern Bangladesh with winds of around 250 km/h (155 mph). The storm forced a 6-metre (20 ft) storm surge inland over a wide area, killing at least 138,866 people and leaving as many as 10 million homeless.[6] Later in the decade, in 1994, another cyclone with a velocity of 210 kilometres (130 mi) per hour struck the coastal area of Cox's Bazar causing extensive damage to the districts of Cox's Bazaar and Bandarban. As a result of the early warning and subsequent evacuation of about 450,000 people, the loss of life was minimal. According to official estimates 133 (including 84 refugees) died and 3,559 were injured.[7]
From July to September 1998, Bangladesh suffered extensive flooding. Over 75% of the total area of the country was flooded, including half of Dhaka.[8] It was similar to the catastrophic flood of 1988, in terms of the extent of the flooding. 30 million people were made homeless and the death toll reached over a thousand.[8] The flooding caused contamination of crops and animals and unclean water resulted in cholera and typhoid outbreaks. About 700,000 hectares of crops were destroyed,[9]
Economy
National Income and Balance of Payment
Bangladesh GDP was USD 42.4 billion in 1990, which grew to USD 63.6 billion in 1999 (in 2010 constant dollar) signifying a 4.1% annual growth. Agricultural Sector contributed to 32.8% of GDP in the beginning of the decade, which decreased to 23.8% by the end. During the same period contribution from the industrial sector increased from 20.7% to 23.5% and that of the service sector increased from 46.6% to 52.7%.[4] Per capita GDP increased from USD 399 to USD 493 (in 2010 constant dollar).
According to World Development Indicators published by the World Bank,[4] on 2010 constant dollar basis, Bangladesh used to export USD 1.3 billion (5.9% of GDP) worth of goods and services as of 1990, which grew at annual average rate of 10.2% to USD 3.5 billion (11.8% of GDP) in 1999. During the same time import of goods and services grew from USD 3.1 billion (13.1% of GDP) to USD 5.8 billion (16.6% of GDP). Over the decade, Foreign Direct Investment and Personal Remittances Receipt averaged 0.12% and 3.02% of GDP; while, total Reserve averaged at 13.3% of external debt and 3.8 month's coverage of import.
Gross National Income (at 2010 constant dollar) grew from USD 43.3 billion to USD 65.7 billion over the decade. At the beginning of this period External Debt stock (of which concessional debt was 90.6%) was 38.1% of Gross National Income (GNI) and External Debt Service burden was 2.3% of GNI. By the end of the decade, External Debt stock (of which concessional debt now was 95.1%) stood at 31.1% of GNI and External Debt Service burden was 1.3% of the same. During the same period Military expenditure increased from 1.2% to 1.5% of GNI.[4]
Agriculture
Aggregate value addition from agricultural sector was USD 9.7 billion in 1990 (in 2010 constant USD), which grew at average annual rate of 2.2% to USD 12.1 billion by 1999 (in the same constant USD).[4] During this decade, crop production grew at an annual average rate of 2.5% driven by cereal production increase from 27.7 million metric tons to 36.4 million (implying annual growth of 2.8%) - enabled by improvement in cereal yield from 2490.6 kg per hectare to 3116.4 kg. At the same time livestock production grew at 3.5% per annum and fisheries production increased at annual rate of 6.3%. Altogether these contributed to overall food production increase by annualized rate of 2.7%.[4]
Industrial and Service Sectors
Net value addition from industrial sector, which stood at USD 7.1 billion in 1990 (in 2010 constant USD), grew at average annual rate of 6.4% to USD 13.2 billion by 1999 (in the same constant USD basis). Manufacturing sector contributed 64.9% of industrial value added in the beginning of this period and it gradually changed to 65.3% by the end. There were 4,094 recorded industrial design applications by Bangladeshi residents in this decade, more than three times that from earlier decade.[4] In 1989-90 there were 24,283 industrial establishments in the country employing 1.08 million staffs. By 1999-2000 the number of establishments grew to 24,752 and employment in the sector grew to 2.26 million.[10]
On the other hand, net value addition from the service sector amounting USD 23.6 billion in 1990, also grew at average annual rate of 3.7% and stood at USD 34.0 billion by 1999 (in 2010 constant USD).[4] Major Businesses / enterprises that started journey in this decade in Bangladesh include Eskayef and Nassa Group in 1990, Confidence Group in 1991, Renata in 1993, Banglalink and Kazi Farms in 1996, Grameenphone and Robi in 1997 and Incepta in 1999.
Infrastructure
Transportation and Communication

The road transport sector experienced rapid changes in the 1990s. Town services as well as inter-city bus transport and private taxicab services significantly improved through introduction of many large bodied modern buses.[11] There were only 133,253 motor vehicles in Bangladesh in 1985 and the number rose to 405,919 in 1999.[12] The construction of Bangabandhu Jamuna Bridge was completed in the second half of the 1990s and the bridge was opened to traffic in 1998. Other important bridges constructed in the 1990s included the Dhalla bridge, the 4th Bangladesh-China Friendship bridge, the Langalbanda bridge and the second Buriganga bridge that linked the national highways and contributed to substantial increase in road traffic.[12] Although the railway network benefited from the increased connectivity from Jamuna Bridge, the sector continued to lose share. The share of the railway sector in passenger traffic declined from 50% in the 1960s to 12% in 1990s and in freight traffic over the same period from 40% to 7%. Due to small volume of traffic and resulting low profitability Faridpur-Pukuria, Bheramara-Raita, Feni-Belonia, and Rupsa-Bagerhat sections of the railway line were closed between 1994 and 1997.[13] Air Transport sector also did not grow much in this decade. As of 1989, there were 14,600 registered carrier departures worldwide which came down to 5,900 by 1999. During the same period number of passenger carried slightly increased from 1.00 million to about 1.22 million per annum.[4]
In the beginning of the decade there were 218,000 fixed telephone line subscription in the country - which increased to 432,968 by the end signifying 0.34 lines per 100 people. By 1999 there were also 149,000 mobile cellular subscriptions signifying 0.12 lines per 100 people. [4]
Energy
In 1990 per capital electric power consumption was 48.4 kWh, which increased to 94.3 kWh by 1999. During the same period per capita energy usage increased from 120.0 kg of oil equivalent to 136.8 kg and fossil fuel energy consumption increased from 45.5% to 57.3% of total.
In 1990 the electricity produced in the country was coming from: hydroelectric sources: 11.4%, natural gas sources: 84.3% and oil sources: 4.3%. By 1999 the distribution changed to - hydroelectric sources: 5.8%, natural gas sources: 85.0% and oil sources: 9.3%.[4]
Financial Services
After addressing the loan recovery issue in the banking sector in the 1980s (see here), from 1990, the Government pursued broader Financial Sector Reform Programs. These reforms include flexible interest rate, convertibility of “Taka”, introduction of 91 days bill, recapitalization of banks, new procedure for loan classification, and strengthening the money and capital market. This helped improve capital adequacy, governance, regulation, supervision and payment system in the economy. [14] New banks starting operations in this decade were: Eastern Bank in 1992, National Credit and Commerce Bank in 1993, Prime Bank, South-east Bank, Dhaka Bank, Al-Arafah Islami Bank and Social Investment Bank in 1995, Premier Bank and Dutch-Bangla Bank in 1996, Mercantile Bank, Standard Bank, One Bank, ExIm Bank, Bangladesh Commerce Bank, Mutual Trust Bank, Trust Bank, Bank Asia and First Security Bank in 1999.[15]
The insurance sector underwent reforms as well. The Insurance Corporations (Amendment) Act 1990 allowed private sector insurance companies to underwrite 50% of the insurance business emanating from the public sector and to place up to 50% of their reinsurance with any reinsurer of their choice, at home or abroad, keeping the remaining for placement with the Sadharan Bima Corporation.[16]
Meanwhile, a new Stock Exchange was established in Chittagong in 1995 to facilitate Capital market in the port city.[17] The regulatory environment was inadequate and market regulations were outdated and not systematically enforced. In this milieu of weak institutional structure and inadequate governance, the capital market experienced its first speculative bubble and burst in 1996-1997. Investors who were affected due to the bubble and burst stayed away from the market for the next several years.[18]
Education

The establishment of democratic regime had it's mark on the education sector as well. In the beginning of the decade many public schools were made double shift, new teaching posts were created, Female students’ stipend programme was introduced, government subsidy in monthly pay order (MPO) was increased and a new assessment system at SSC examination was introduced. During mid 1990s, the secondary school curriculum was updated, about 150,000 teachers received short-term training in the new curriculum and teacher training institutes experienced a major uplift. At the end of 1990s, ‘Shamsul Haque Education Commission 1997’ was formed.[19]
In the beginning of the decade about 3.5 million primary-school-age children remained outside school, but this number continued to decline.[20] Based on World Bank data,[4] in 1990, there were 3.59 million secondary school students (including higher secondary) in the country, which significantly grew to 9.91 million by the end of the decade. Secondary school enrollment rate drastically improved from 20.4 % to 46.6 % during the same period. Thanks to the new initiatives, over these years ratio of female students in secondary education increased from 33.0 % to 49.0 % and the number of teachers covering the strudnts grew from 131 to 265 thousand.
The secondary and higher secondary education administration for the country, used to be managed by 4 general education boards, namely Dhaka, Rajshahi, Comilla and Jessore; a Technical Education Board and a Madrasah Education Board. To strengthen and expand the supervision of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education Examinations, Chittagong Board was set up in 1995, and then two additional education boards, Barisal and Sylhet were set up in 1999.[21]
In the early 1990s the tertiary education in the country was fully managed in the public sector. Five general purpose universities (DU, RU, CU, JU and IU) along with 4 specialized universities - BUET, BAU and newly opened IUT and SUST catered for the need of higher education in the country. The Khulna University (KU) formally inaugurated academic activities on 25 November 1991. Bangladesh Open University and National University of Bangladesh were established in 1992 to further the causes of distant learning. Three other public sector specialized universities, namely Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University (BSMRAU), Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science & Technology University (HSTU) and Mawlana Bhashani Science and Technology University (MBSTU) were established by the end of the decade. Furthermore, Institute of Postgraduate Medicine and Research (IPGMR) - the authoritative body in medical education in the country - was renamed as Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University (BSMMU) by the Act 1, 1998 of Jatiyo Sangshad.
Perhaps the most transformative change in the tertiary education sector in this decade was opening up to the private sector. Establishment of private universities in Bangladesh was initiated after the institution of the Private University Act 1992 [22] and by the end of the decade, at least 17 private universities had started their operations, including IUBAT, NSU, USTC, CWU, IUB, AIUB, AUST, DIU, IIUC, AUB and EWU. However, most of these universities started their operation in limited scale at rented premises which drew considerable criticism regarding the quality of higher education in private sector.[23]
See also
Years in Bangladesh in the decade of
References
- "Ershad, Lt. General Hussein M - Banglapedia". en.banglapedia.org. Retrieved 2018-02-05.
- Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs (March 2008). "Background Note: Bangladesh". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 11 June 2008. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Siddiqui, K. (2012). "Local Government". Banglapedia. Retrieved 17 Feb 2020.
- "World Development Indicators". The World Bank. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "Climate Change Knowledge Portal". The World Bank Group. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
- Unattributed (2008). "The Worst Natural Disasters by Death Toll" (PDF). NOAA Backgrounder. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- "Bangladesh - Cyclone May 1994 UN DHA Information Reports 1-4". UN Department of Humanitarian Affairs. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- Bangladesh floods recede, but death toll rises, 17 September 1998
- "World: South Asia Bangladesh floods rise again", BBC News, 24 August 1998
- Report on Survey of Manufacturing Industries 2005-06. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
- "Transport". Banglapedia. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- "Road Transport". Banglapedia. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- "Railway". Banglapedia. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- "The Current State of Financial Sector of Bangladesh: An Analysis" (PDF). AIUB. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- "Banking System, Modern". Banglapedia. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- "Insurance". Banglapedia. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- Muhammad Abdul Mazid (2012). "Chittagong Stock Exchange". In Islam, Sirajul; Miah, Sajahan; Khanam, Mahfuza; Ahmed, Sabbir (eds.). Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. ISBN 984-32-0576-6. OCLC 52727562. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- Amit, Sajid (22 October 2017). "Bangladesh capital markets: An overview". The Financial Express. Retrieved 4 August 2020.
- Rahman, M. M.; Hamzah, M. I. M.; Meerah, T. S. M.; Rahman, Mizan (February 2020). "Historical Development of Secondary Education in Bangladesh: Colonial Period to 21st Century" (PDF). International Education Studies. 3 (1): 114–125. Retrieved 2021-01-26.
- "Bangladesh Education Stats". NationMaster. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- "Education Board Bangladesh". www.educationboard.gov.bd. Retrieved 2020-12-28.
- "Private University Act 1992". Archived from the original on 2003-04-25. Retrieved 2008-03-28.
- Wadood, Syed Naimul. (2006). The Public-Private University Debate in the Higher Education Sector in Bangladesh. University Library of Munich, Germany, MPRA Paper.