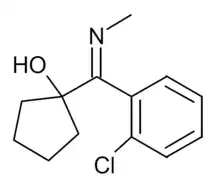
1-(2-Chloro-N-methylbenzimidoyl)cyclopentanol
1-(2-Chloro-N-methylbenzimidoyl)cyclopentanol, sometimes misleadingly referred to as hydroxylimine hydrochloride, is a chemical compound which is the final intermediate in the synthesis of ketamine, an anaesthetic drug which is also subject to recreational abuse. This chemical intermediate is not active as a drug in its own right, and is legal in most countries, but is readily converted into ketamine by dissolving it in a suitable high-boiling point solvent and heating, with no other chemicals required.[1][2] This has made it subject to illicit trade as a drug precursor, and it has sometimes been seized by law enforcement agencies in significant quantities, leading to it being specifically banned as a controlled drug precursor in some jurisdictions such as Taiwan.[3][4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.169.732 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H16ClNO |
| Molar mass | 237.73 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- US patent 3254124, Stevens CL, "Aminoketones and methods for their production", issued 1966-05-31, assigned to Parke Davis & Co.
- Dimitrov I, Denny WA, Jose J (2018). "Syntheses of Ketamine and Related Analogues: A Mini Review". Synthesis. 50 (21): 4201–4215. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1609935.
- "200 kg of ketamine precursor seized at Taoyuan Airport". Taiwan News. 1 January 2009.
- "Taiwan catches 2 tons of drugs hidden inside machinery from China". Taiwan News. 31 March 2018.