1,2-Cyclohexanedione
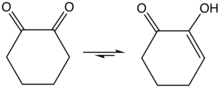
1,2-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. It is one of three isomeric cyclohexanediones. It is a colorless compound that is soluble in a variety of organic solvents. It can be prepared by oxidation of cyclohexanone by selenium dioxide.[1] The enol is about 1 kcal/mol more stable than the diketo form.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclohexane-1,2-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.050 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 112.128 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white, waxy solid |
| Density | 1.1305 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 40 °C |
| Boiling point | 194 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Numerous diimine and dioxime ligands have been prepared from this diketone. It condenses with 1,2-diamines to give diaza heterocycles.
References
- Hach, Clifford C.; Banks, Charles V.; Diehl, Harvey (1952). "1,2-Cyclohexanedione Dioxime". Org. Synth. 32: 35. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.032.0035.
- Jana, Kalyanashis; Ganguly, Bishwajit (2018). "DFT Study to Explore the Importance of Ring Size and Effect of Solvents on the Keto–Enol Tautomerization Process of α- and β-Cyclodiones". ACS Omega. 3 (7): 8429–8439. doi:10.1021/acsomega.8b01008. PMC 6644555. PMID 31458971.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.